Muscles of the Head and Neck - Listed Alphabetically
|
| Muscle |
Origin |
Insertion |
Action |
Innervation |
Artery |
Notes |
Image |
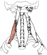
| anterior scalene |
anterior tubercles of the transverse processes of vertebrae C3-C6 |
scalene tubercle of the first rib |
elevates the first rib; flexes and laterally bends the neck |
brachial plexus, C5-C7 |
ascending cervical a., a branch of the thyrocervical trunk |
a muscle of inspiration; an important landmark of the neck; it is located
between the subclavian vein and the subclavian artery; the roots of the brachial
plexus pass posterior to it; the phrenic nerve crosses its anterior surface |
 |
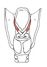
| aryepiglottic |
apex (superior part) of the arytenoid cartilage |
epiglottis |
draws the epiglottis posteriorly and downward during swallowing |
inferior laryngeal nerve, from recurrent laryngeal nerve, a branch of the
of vagus (X) |
laryngeal br. of the superior thyroid a. |
the mucosa is raised by the underlying aryepiglottic m. to form the aryepiglottic
fold |
 |
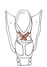
| arytenoid, oblique |
muscular process of the arytenoid cartilage |
posterior surface of the contralateral arytenoid cartilage, near its apex |
draws arytenoid cartilages together, adducting the vocal folds |
inferior laryngeal nerve, from recurrent laryngeal nerve, a branch of the
of vagus (X) |
laryngeal br. of the superior thyroid a. |
the oblique arytenoid m. lies posterior to the transverse arytenoid m.;
the arytenoideus is often considered to be one muscle with oblique and transverse
fibers |
 |
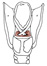
| arytenoid, transverse |
posterior surface of the arytenoid cartilage |
posterior surface of the contralateral arytenoid cartilage |
draws arytenoid cartilages together, adducting the vocal folds |
inferior laryngeal nerve, from recurrent laryngeal nerve, a branch of the
vagus nerve (X) |
laryngeal br. of the superior thyroid a. |
the transverse arytenoid m.lies anterior to the oblique arytenoid m.; the
arytenoideus is often considered to be one muscle with oblique and transverse
parts |
 |
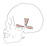
| auricular |
anterior: galea aponeurotica anterior to ear; superior: galea aponeurotica
superior to ear; posterior: mastoid process |
auricle anteriorly, superiorly and posteriorly |
wiggle the ears |
anterior & superior: temporal branches of facial nerve (VII); posterior:
posterior auricular branch of facial nerve (VII) |
superficial temporal a., posterior auricular a. |
the auricular muscles are derived from the mesenchyme of the second pharyngeal
arch, as are the muscles of facial expression |
 |
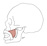
| buccinator |
pterygomandibular raphe, mandible, and the maxilla lateral to the molar
teeth |
angle of mouth and the lateral portion of the upper and lower lips |
pulls the corner of mouth laterally; presses the cheek against the teeth |
buccal branches of the facial nerve (VII) |
facial a. |
although the buccinator is important in mastication, it is innervated by
the buccal branch of the facial nerve and NOT by the buccal nerve from V3 (a
sensory nerve) |
 |
| chondroglossus |
medial side of the lesser horn and body of the hyoid bone |
ascends to blend with the intrinsic tongue musculature |
pulls the sides of the tongue down |
hypoglossal nerve (XII) |
lingual a. |
chondroglossus is often considered to be part of the hyoglossus muscle |
 |
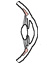
| ciliary |
meridional fibers: scleral spur; circular fibers: encircle the ciliary process |
meridional fibers: ciliary process; circular fibers: encircle the ciliary
process |
relaxes the suspensory ligament of the lens |
parasympathetic fibers in the oculomotor nerve (III), synapsing in the ciliary
ganglion |
ophthalmic a. |
relaxation of the suspensory ligament allows the lens to thicken for accommodation
(near vision) |
 |
| constrictor, inferior pharyngeal |
oblique line of the thyroid cartilage, lateral surface of cricoid cartilage |
midline pharyngeal raphe |
constricts pharyngeal cavity |
vagus (X), via the pharyngeal plexus, with aid from the superior laryngeal
and recurrent laryngeal nerves |
ascending pharyngeal a., superior thyroid a., inferior thyroid a. |
the most external of the three pharyngeal constructor mm. |
 |
| constrictor, middle pharyngeal |
lesser and greater horns of the hyoid bone and the inferior part of the
stylohyoid ligament |
midline pharyngeal raphe |
constricts the pharyngeal cavity |
vagus (X), via the pharyngeal plexus |
ascending pharyngeal a. |
of the three pharyngeal constrictors, this one is intermediate in both superior/inferior
position and depth |
 |
| constrictor, superior pharyngeal |
medial pterygoid plate, pterygoid hamulus, pterygomandibular raphe, mylohyoid
line of mandible |
pharyngeal tubercle and midline pharyngeal raphe |
constricts the pharyngeal cavity |
vagus (X), via the pharyngeal plexus |
ascending pharyngeal a. |
the most internal of the three pharyngeal constructor mm. |
 |
| corrugator |
medial part of the supercillary arch |
skin of the medial half of the eyebrow |
pulls eyebrows together medially |
temporal branch of the facial nerve (VII) |
supratrochlear a. |
this muscle causes the furrowed brow of the worried look |
 |
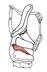
| cricoarytenoid, lateral |
arch of the cricoid cartilage |
muscular process of the arytenoid cartilage |
draws the muscular process of the arytenoid cartilage anteriorly, which
pivots the arytenoid cartilage and adducts the vocal folds |
inferior laryngeal nerve, from the recurrent laryngeal nerve, a branch of
the vagus nerve (X) |
superior laryngeal a., cricothyroid branch of the superior thyroid a. |
an antagonist of the posterior cricoarytenoid m.; the arteries that supply
the larynx anastomose within the larynx to supply the mucous membranes and
muscles |
 |
| cricoarytenoid, posterior |
posterior surface of the lamina of the cricoid cartilage |
muscular process of the arytenoid cartilage |
draws the muscular process posteriorly, which pivots the arytenoid cartilage
and abducts the vocal folds |
inferior laryngeal nerve, from the recurrent laryngeal nerve, a branch of
the vagus nerve (X) |
superior laryngeal a., cricothyroid branch of the superior thyroid a. |
the posterior cricoarytenoid is the only ABductor of the vocal folds; the
arteries that supply the larynx anastomose within the larynx to supply the
mucous membranes and muscles |
 |
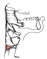
| cricopharyngeus |
lateral surface of the cricoid cartilage |
midline pharyngeal raphe |
constricts the pharyngeal cavity and the entrance to the esophagus |
recurrent laryngeal nerve, a branch of the vagus nerve (X) |
cricothyroid branch of the superior thyroid a., ascending pharyngeal a. |
cricopharyngeus represents the lowest fibers of the inferior pharyngeal
constrictor; it is continuous with the esophagus below and marks the beginning
of it |
 |
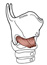
| cricothyroid |
arch of the cricoid cartilage |
inferior border of the thyroid cartilage |
draws the thyroid cartilage forward, lengthening the vocal ligaments |
external branch of superior laryngeal nerve, a branch of the vagus nerve
(X) |
cricothyroid branch of the superior thyroid a. |
this is the only intrinsic muscle of the larynx that is not supplied by
the recurrent laryngeal n.; ALL other laryngeal muscles are innervated by recurrent
laryngeal nerve, via its inferior laryngeal branch |
 |
| depressor anguli oris |
oblique line of the mandible |
angle of the mouth |
pulls the corner of the mouth downward |
marginal mandibular & buccal branches of the facial nerve (VII) |
inferior labial branch of the facial a., mental a. |
a "frown" muscle |
 |
| depressor labii inferioris |
anterior surface of the mandible |
skin of the lower lip |
depresses the lower lip |
marginal mandibular branch of the facial nerve (VII) |
inferior labial branch of the facial a., mental a. |
this muscle is used to bare the lower incisor teeth |
 |
| depressor septi |
maxilla near the midline above the incisor teeth |
nasal septum |
depresses the nasal septum; involved in flaring the nostrils |
buccal branch of facial nerve (VII) |
superior labial branch of the facial a. |
depressor septi is considered a part of the nasalis m. |
 |
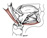
| digastric |
anterior belly: digastric fossa of the mandible; posterior belly: mastoid
notch of the temporal bone |
body of the hyoid via a fibrous loop over an intermediate tendon |
elevates the hyoid bone; depresses the mandible |
anterior belly: mylohyoid nerve, from the mandibular division of the trigeminal
nerve (V); posterior belly: facial nerve (VII) |
anterior belly: submental a.; posterior belly: occipital a. |
the digastric m. forms two sides of the submandibular triangle; it is formed
from mesenchyme derived from the first two pharyngeal arches, hence its dual
innervation |
 |
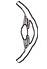
| dilator pupillae |
outer margin of iris |
inner margin of iris |
dilates the pupil |
sympathetic fibers via short ciliary nerves, synapsing in superior cervical
sympathetic ganglion |
ophthalmic a. |
none |
 |
| epicranius |
frontalis: galea aponeurotica; occipitalis: superior nuchal line |
frontalis: skin of the eyebrows; occipitalis: galea aponeurotica |
elevates the eyebrows and wrinkles the forehead |
frontalis: temporal branches of the facial nerve (VII); occipitalis: posterior
auricular branch of the facial nerve (VII) |
frontalis: supraorbital and supratrochlear aa.; occipitalis: occipital a.
|
the frontalis and occipitalis muscles are two bellies of the epicranius
muscle; also known as: occipitofrontalis m. |
 |
| frontalis |
galea aponeurotica |
skin of the eyebrow |
elevates the eyebrows and wrinkles the forehead |
temporal branches of the facial nerve (VII) |
supraorbital and supratrochlear aa. |
frontalis is the anterior belly of the epicranius muscle |
 |
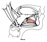
| genioglossus |
mental spine on the inner aspect of the mental symphysis |
fans out to insert into the tongue from the tip to the base |
protrudes the tongue (inferior fibers); depresses tongue (middle fibers) |
hypoglossal nerve (XII) |
lingual a. |
an extrinsic muscle of the tongue; XII innervates all tongue muscles except
palatoglossus [innervated by vagus (X), as are most of the palate and pharynx
muscles]; genioglossus is used to test the function of cranial nerve XII |
 |
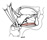
| geniohyoid |
mental spines of the mandible |
body of the hyoid bone |
elevates the hyoid bone; depresses the mandible |
ventral primary ramus of spinal nerve C1 via fibers carried by the hypoglossal
nerve |
lingual a., submental a. |
thyrohyoid and geniohyoid receive ansa cervicalis fibers that travel with
the hypoglossal nerve distal to the superior limb of the ansa cervicalis |
 |
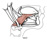
| hyoglossus |
upper border of the greater horn of the hyoid and body of the hyoid bone |
spreads out into the intrinsic muscles of the tongue |
depresses the sides of the tongue; retracts the tongue |
hypoglossal nerve (XII) |
lingual a. |
an extrinsic muscle of the tongue |
 |
| inferior oblique |
floor of the orbit lateral to the lacrimal groove |
sclera on the inferior surface of the eyeball |
elevates and abducts the corneal part of the eye; rotates the superior pole
of the iris laterally; when the eye is adducted, this muscle elevates the cornea |
oculomotor nerve (III), inferior division |
ophthalmic a. |
clinicians examining the eye will ask the patient to look toward the bridge
of the nose to test the function of this muscle |
 |
| inferior pharyngeal constrictor |
oblique line of the thyroid cartilage, lateral surface of cricoid cartilage |
midline pharyngeal raphe |
constricts pharyngeal cavity |
vagus (X), via the pharyngeal plexus, with aid from the superior laryngeal
and recurrent laryngeal nerves |
ascending pharyngeal a., superior thyroid a., inferior thyroid a. |
the most external of the three pharyngeal constructor mm. |
 |
| inferior rectus |
common tendinous ring at the apex of the orbit |
sclera on the inferior surface of the eyeball |
depresses and adducts the corneal part of the eyeball; rotates the superior
pole of the iris laterally |
oculomotor nerve (III), inferior division |
ophthalmic a. |
because this muscle approaches the eyeball from a medial direction, it has
a rotational action on the iris |
 |
| lateral cricoarytenoid |
arch of the cricoid cartilage |
muscular process of the arytenoid cartilage |
draws the muscular process of the arytenoid cartilage anteriorly, which
pivots the arytenoid cartilage and adducts the vocal folds |
inferior laryngeal nerve, from the recurrent laryngeal nerve, a branch of
the vagus nerve (X) |
superior laryngeal a., cricothyroid branch of the superior thyroid a. |
an antagonist of the posterior cricoarytenoid m.; the arteries that supply
the larynx anastomose within the larynx to supply the mucous membranes and
muscles |
 |
| lateral pterygoid |
superior head: greater wing of the sphenoid bone; inferior head: lateral
surface of the lateral pterygoid plate |
superior head: capsule and & articular disk of the temporomandibular joint;
inferior head: neck of the mandible |
protracts the mandible; opens the mouth; active in grinding actions of chewing |
lateral pterygoid branch of the mandibular division of the trigeminal nerve
(V) |
pterygoid branch of the maxillary a. |
the only one of the muscles of mastication that opens the mouth; the superior
head of lateral pterygoid is sometimes called sphenomeniscus due to its insertion
into the disc of the temporomandibular joint |
 |
| lateral rectus |
common tendinous ring at the apex of the orbit |
sclera on the lateral surface of the eyeball |
abducts the corneal part of the eyeball |
abducens nerve (VI) |
ophthalmic a. |
loss of function of the abducens nerve will cause the eye to be abducted |
 |
| levator anguli oris |
canine fossa of the maxilla |
angle (corner) of the mouth |
elevates the angle of the mouth |
buccal branch of the facial nerve (VII) |
infraorbital a., superior labial branch of the facial a. |
a "smile" muscle |
 |
| levator labii superioris |
inferior margin of the orbit |
skin of the upper lip |
elevates the upper lip |
buccal branch of the facial nerve (VII) |
infraorbital a., superior labial branch of the facial a. |
levator labii superioris is used to bare the upper incisor teeth, as in
a sneer |
 |
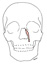
| levator labii superioris alaque nasi |
frontal process of the maxilla |
ala of the nose and skin of the upper lip |
elevates the upper lip and flares the nostril |
buccal branch of the facial nerve (VII) |
infraorbital a., superior labial branch of the facial a. |
none |
 |
| levator palpebrae superioris |
apex of the orbit above the optic canal |
skin and fascia of upper eyelid and the superior tarsal plate |
elevates the upper eyelid |
oculomotor nerve (III) and sympathetics (to the superior tarsal portion) |
ophthalmic a. |
fibers inserting into the superior tarsal plate are called superior tarsal
muscle and are smooth muscle; lesion of the sympathetic supply causes slight
ptosis (drooping of the eyelid) |
 |
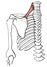
| levator scapulae |
transverse processes of C1-4 vertebrae |
medial border of the scapula from the superior angle to the spine |
elevates scapula |
dorsal scapular nerve (C5); the upper part of the muscle receives branches
of C3 & C4 spinal nerves |
dorsal scapular a. |
named for its action |
 |
| levator veli palatini |
apex of the petrous part of the temporal bone and the medial surface of
the auditory tube cartilage |
muscles and fascia of the soft palate; palatine aponeurosis |
elevates the soft palate |
vagus nerve (X) via the pharyngeal plexus |
ascending pharyngeal a. |
a derivative of the fourth pharyngeal arch |
 |
| linguae, longitudinalis |
within tongue |
within tongue near the apex |
shapes the tongue for speech and mastication |
hypoglossal nerve (XII) |
lingual a. |
an intrinsic muscle of the tongue; longitudinalis has superior and inferior
subdivisions that span the length of the tongue |
 |
| linguae, transversus |
within tongue |
within tongue |
compresses the sides of the tongue; shapes the tongue for speech and mastication |
hypoglossal nerve (XII) |
lingual a. |
an intrinsic muscle of the tongue whose fibers run transversely |
Image Not Available |
| linguae, verticalis |
within tongue |
within tongue |
shapes the tongue for speech and mastication |
hypoglossal nerve (XII) |
lingual a. |
an intrinsic muscle of the tongue whose fibers run superoinferiorly |
 |
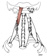
| longus capitis |
anterior tubercles of vertebrae C3-6 |
basilar portion of the occipital bone |
flex the head and neck |
cervical plexus, ventral primary rami of spinal nerves C1-4 |
deep cervical a. |
none |
 |
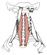
| longus colli |
anterior tubercles and anterior surfaces of the bodies of vertebrae C3-T3 |
anterior arch of atlas, anterior tubercles of C5-6, anterior surfaces of
bodies of vertebrae C2-4 |
flex neck, rotate and laterally bend neck |
cervical and brachial plexus, C2-7 |
deep cervical a. |
none |
 |
| masseter |
zygomatic arch and zygomatic bone |
lateral surface of the ramus and angle of the mandible |
elevates the mandible |
nerve to the masseter, from the mandibular division of the trigeminal nerve
(V) |
masseteric branch of the maxillary a. |
a powerful chewing muscle |
 |
| medial pterygoid |
medial surface of the lateral pterygoid plate, pyramidal process of the
palatine bone, tuberosity of the maxilla |
medial surface of the ramus and angle of the mandible |
elevates and protracts the mandible |
medial pterygoid branch of the mandibular division of the trigeminal nerve
(V) |
pterygoid branch of the maxillary a. |
this muscle mirrors the masseter m. in position and action with the ramus
of the mandible between the two mm. |
 |
| medial rectus |
common tendinous ring at the apex of the orbit |
sclera on the medial surface of the eyeball |
adducts the corneal part of the eyeball |
oculomotor nerve (III) (inferior division) |
ophthalmic a. |
this muscle directly opposes the action of the lateral rectus m. |
 |
| mentalis |
anterior surface of the mandible near the mental symphysis (midline) |
skin of the chin |
elevates the lower lip and skin of chin |
marginal mandibular branch of the facial nerve (VII) |
mental a., inferior labial branch of the facial a. |
|
 |
| middle pharyngeal constrictor |
lesser and greater horns of the hyoid bone and the inferior part of the
stylohyoid ligament |
midline pharyngeal raphe |
constricts the pharyngeal cavity |
vagus (X), via the pharyngeal plexus |
ascending pharyngeal a. |
of the three pharyngeal constrictors, this one is intermediate in both superior/inferior
position and depth |
 |
| middle scalene |
posterior tubercles of the transverse processes of vertebrae C2-C7 |
upper surface of the first rib behind the subclavian artery |
elevates the first rib; flexes and laterally bends the neck |
brachial plexus, C3-C8 |
ascending cervical a. |
a muscle of respiration (inspiratory); also called scalenus medius; penetrated
by the dorsal scapular n. and long thoracic n. |
 |
| musculus uvulae |
posterior nasal spine |
mucosa of the uvula |
shortens the uvula |
vagus nerve (X) via pharyngeal plexus |
lesser palatine a. |
the soft palate and uvula resist the upward pressure of the tongue during
swallowing |
 |
| mylohyoid |
mylohyoid line of mandible |
midline raphe and body of the hyoid bone |
elevates the hyoid bone and the tongue; depresses the mandible |
mylohyoid nerve from the inferior alveolar nerve, a branch of the mandibular
division of the trigeminal nerve (V) |
mylohyoid branch of the inferior alveolar a. |
the nerve to mylohyoid also innervates the anterior belly of digastric m.;
both muscles are derivatives of the second pharygneal arch |
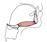 |
| nasalis |
maxilla above the incisor teeth and the canine teeth |
ala of the nose and midline aponeurosis |
flattens the nose, flare the nostrils |
buccal branch of the facial nerve (VII) |
superior labial branch of the facial a. |
nasalis has two subsidiary parts: nasalis pars alaris and pars transversa |
 |
| nasalis pars alaris |
maxilla above the canine teeth |
ala of the nose |
flares the nostrils |
buccal branch of facial nerve (VII) |
superior labial branch of the facial a. |
a subdivision of the nasalis m. |
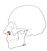 |
| nasalis pars transversa |
maxilla above the incisor teeth |
midline aponeurosis |
flattens the nose |
buccal branch of facial nerve (VII) |
superior labial branch of the facial a. |
a subdivision of the nasalis m. |
 |
| oblique arytenoid |
muscular process of the arytenoid cartilage |
posterior surface of the contralateral arytenoid cartilage, near its apex |
draws arytenoid cartilages together, adducting the vocal folds |
inferior laryngeal nerve, from recurrent laryngeal nerve, a branch of the
of vagus (X) |
laryngeal br. of the superior thyroid a. |
the oblique arytenoid m. lies posterior to the transverse arytenoid m.;
the arytenoideus is often considered to be one muscle with oblique and transverse
fibers |
 |
| oblique, inferior |
floor of the orbit lateral to the lacrimal groove |
sclera on the inferior surface of the eyeball |
elevates and abducts the corneal part of the eye; rotates the superior pole
of the iris laterally; when the eye is adducted, this muscle elevates the cornea |
oculomotor nerve (III), inferior division |
ophthalmic a. |
clinicians examining the eye will ask the patient to look toward the bridge
of the nose to test the function of this muscle |
 |
| oblique, superior |
apex of the orbit above the optic canal |
sclera on the posterior superior surface of the eyeball |
depresses and abducts the eyeball; rotates the superior pole of the iris
medially |
trochlear nerve (IV) |
ophthalmic a. |
passes through a fibrocartilagenous pulley known as the trochlea; when the
eye is adducted, this muscle moves the cornea inferiorly |
 |
| occipitalis |
superior nuchal line |
galea aponeurotica |
pulls the scalp posteriorly; elevates the eyebrows |
posterior auricular branch of the facial nerve (VII) |
occipital a. |
occipitalis is the posterior belly of the epicranius muscle |
 |
| occipitofrontalis |
frontalis: galea aponeurotica; occipitalis: superior nuchal line |
frontalis: skin of the eyebrows; occipitalis: galea aponeurotica |
elevates the eyebrows and wrinkles the forehead |
frontalis: temporal branches of the facial nerve (VII); occipitalis: posterior
auricular branch of the facial nerve (VII) |
frontalis: supraorbital and supratrochlear aa.; occipitalis: occipital a.
|
the frontalis and occipitalis muscles are two bellies of the occipitofrontalis
muscle; also known as: epicranius m. |
 |
| omohyoid |
inferior belly: upper border of the scapula medial to the scapular notch;
superior belly: intermediate tendon |
inferior belly: intermediate tendon; superior belly: lower border of the
hyoid bone lateral to the sternohyoid insertion |
depresses/stabilizes the hyoid bone |
ansa cervicalis |
transverse cervical a. |
the intermediate tendon of omohyoid is tethered to the clavicle by a fascial
sling |
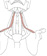 |
| orbicularis oculi |
orbital part: medial orbital margin and the medial palpebral ligament; palpebral
part: medial palpebral ligament |
orbital part: skin of the lateral cheek; palpebral part: lateral palpebral
raphe |
closes the eyelids |
temporal & zygomatic branches of the facial nerve (VII) |
supraorbital a., supratrochlear a., infraorbital a., angular branch of the
facial a. |
activated involuntarily in the blink reflex; the palpebral part is active
in normal blinking and the orbital part is used to forcefully close the eye |
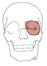 |
| orbicularis oris |
skin and fascia of lips and the area surrounding the lips |
skin and fascia of the lips |
purses the lips |
buccal branch of the facial nerve (VII) |
superior and inferior labial branches of the facial a., mental a., infraorbital
a. |
the "kissing" muscle |
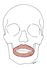 |
| palatoglossus |
palatine aponeurosis |
side of the tongue, entering it from above |
elevates and retracts the tongue |
vagus nerve (X) via the pharyngeal plexus |
tonsilar branch of the facial a., ascending pharyngeal a. |
although palatoglossus sounds like a tongue muscle (and would therefore
be innervated by XII), it is a palatal muscle innervated by X |
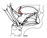 |
| palatopharyngeus |
posterior margin of the bony palate and the palatine aponeurosis |
posterior wall of the pharynx and the posterior margin of the thyroid cartilage |
elevates the larynx |
vagus nerve (X) via pharyngeal plexus |
ascending pharyngeal a. |
palatopharyngeus is part of the inner longitudinal muscle layer of the pharynx |
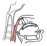 |
| platysma |
fascia overlying the pectoralis major and deltoid muscles |
inferior border of the mandible and skin of lower face |
draws the corners of the mouth down; it aids in depression of the mandible |
cervical branch of the facial nerve (VII) |
facial a. |
platysma is derived from the mesenchyme of the second pharyngeal arch |
 |
| posterior cricoarytenoid |
posterior surface of the lamina of the cricoid cartilage |
muscular process of the arytenoid cartilage |
draws the muscular process posteriorly, which pivots the arytenoid cartilage
and abducts the vocal folds |
inferior laryngeal nerve, from the recurrent laryngeal nerve, a branch of
the vagus nerve (X) |
superior laryngeal a., cricothyroid branch of the superior thyroid a. |
the posterior cricoarytenoid is the only ABductor of the vocal folds; the
arteries that supply the larynx anastomose within the larynx to supply the
mucous membranes and muscles |
 |
| posterior scalene |
posterior tubercles of the transverse processes of vertebrae C5-C7 |
lateral surface of the second rib |
elevates the second rib; flexes and laterally bends the neck |
brachial plexus, C7-C8 |
ascending cervical a. |
a muscle of respiration (inspiratory); it is the longest of the scalene
muscles |
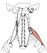 |
| procerus |
nasal bone |
skin between the eyebrows |
depresses the medial corners of the eyebrows |
temporal branch of the facial nerve (VII) |
supratrochlear a. |
none |
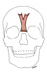 |
| pterygoid, lateral |
superior head: greater wing of the sphenoid bone; inferior head: lateral
surface of the lateral pterygoid plate |
superior head: capsule and & articular disk of the temporomandibular joint;
inferior head: neck of the mandible |
protracts the mandible; opens the mouth; active in grinding actions of chewing |
lateral pterygoid branch of the mandibular division of the trigeminal nerve
(V) |
pterygoid branch of the maxillary a. |
the only one of the muscles of mastication that opens the mouth; the superior
head of lateral pterygoid is sometimes called sphenomeniscus due to its insertion
into the disc of the temporomandibular joint |
 |
| pterygoid, medial |
medial surface of the lateral pterygoid plate, pyramidal process of the
palatine bone, tuberosity of the maxilla |
medial surface of the ramus and angle of the mandible |
elevates and protracts the mandible |
medial pterygoid branch of the mandibular division of the trigeminal nerve
(V) |
pterygoid branch of the maxillary a. |
this muscle mirrors the masseter m. in position and action with the ramus
of the mandible between the two mm. |
 |
| pupillae, dilator |
outer margin of iris |
inner margin of iris |
dilates the pupil |
sympathetic fibers via short ciliary nerves, synapsing in superior cervical
sympathetic ganglion |
ophthalmic a. |
none |
 |
| pupillae, sphincter |
encircles iris |
encircles iris |
constricts the pupil |
parasympathetic fibers of oculomotor nerve (III), synapsing in ciliary ganglion |
ophthalmic a. |
none |
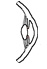 |
| rectus capitis anterior |
lateral mass of atlas |
basilar portion of occipital bone |
flexes the head |
ventral primary ramus of spinal nerve C1 |
deep cervical a. |
none |
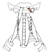 |
| rectus capitis lateralis |
transverse process of atlas |
occipital bone anterolateral to foramen magnum |
laterally bends the head |
ventral primary ramus of spinal nerve C1 |
deep cervical a. |
none |
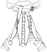 |
| rectus, inferior |
common tendinous ring at the apex of the orbit |
sclera on the inferior surface of the eyeball |
depresses and adducts the corneal part of the eyeball; rotates the superior
pole of the iris laterally |
oculomotor nerve (III), inferior division |
ophthalmic a. |
because this muscle approaches the eyeball from a medial direction, it has
a rotational action on the iris |
 |
| rectus, lateral |
common tendinous ring at the apex of the orbit |
sclera on the lateral surface of the eyeball |
abducts the corneal part of the eyeball |
abducens nerve (VI) |
ophthalmic a. |
loss of function of the abducens nerve will cause the eye to be abducted |
 |
| rectus, medial |
common tendinous ring at the apex of the orbit |
sclera on the medial surface of the eyeball |
adducts the corneal part of the eyeball |
oculomotor nerve (III) (inferior division) |
ophthalmic a. |
this muscle directly opposes the action of the lateral rectus m. |
 |
| rectus, superior |
common tendinous ring at the apex of the orbit |
sclera on the superior surface of the eyeball |
elevates and adducts the eyeball; rotates the superior pole of the iris
medially |
oculomotor nerve (III), superior division |
ophthalmic a. |
because this muscle approaches the eye from a medial position, it causes
the iris to rotate medially |
 |
| risorius |
fascia of the lateral cheek |
skin of the angle (corner) of the mouth |
draws the corner of the mouth laterally |
buccal branches of the facial nerve (VII) |
transverse facial a., facial a. |
risorius is active in expressions of mirth |
 |
| salpingopharyngeus |
inferior surface of the anteromedial end of the auditory tube cartilage |
pharyngeal wall and superior border of the thyroid cartilage along with
the palatopharyngeus m. |
elevates the larynx |
vagus nerve (X) via the pharyngeal plexus |
ascending pharyngeal a. |
like other muscles of the pharyngeal wall, salpingopharyngeus is derived
from the fourth pharyngeal arch |
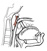 |
| scalene, anterior |
anterior tubercles of the transverse processes of vertebrae C3-C6 |
scalene tubercle of the first rib |
elevates the first rib; flexes and laterally bends the neck |
brachial plexus, C5-C7 |
ascending cervical a., a branch of the thyrocervical trunk |
a muscle of inspiration; an important landmark of the neck; it is located
between the subclavian vein and the subclavian artery; the roots of the brachial
plexus pass posterior to it; the phrenic nerve crosses its anterior surface |
 |
| scalene, middle |
posterior tubercles of the transverse processes of vertebrae C2-C7 |
upper surface of the first rib behind the subclavian artery |
elevates the first rib; flexes and laterally bends the neck |
brachial plexus, C3-C8 |
ascending cervical a. |
a muscle of respiration (inspiratory); also called scalenus medius; penetrated
by the dorsal scapular n. and long thoracic n. |
 |
| scalene, posterior |
posterior tubercles of the transverse processes of vertebrae C5-C7 |
lateral surface of the second rib |
elevates the second rib; flexes and laterally bends the neck |
brachial plexus, C7-C8 |
ascending cervical a. |
a muscle of respiration (inspiratory); it is the longest of the scalene
muscles |
 |
| sphenomeniscus |
greater wing of the sphenoid |
capsule and articular disk of the temporomandibular joint |
pulls the articular disk forward in opening of the mouth |
lateral pterygoid branch of mandibular division of trigeminal nerve (V) |
pterygoid branch of the maxillary a. |
sphenomeniscus is another name for the superior belly of the lateral pterygoid
m. |
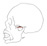 |
| sphincter pupillae |
encircles iris |
encircles iris |
constricts the pupil |
parasympathetic fibers of oculomotor nerve (III), synapsing in ciliary ganglion |
ophthalmic a. |
none |
 |
| splenius |
ligamentum nuchae and spines C7-T6 |
capitis: mastoid process & superior nuchal line laterally; cervicis: posterior
tubercles of C1-3 |
extends and laterally bends neck and head; rotates head to same side |
dorsal primary rami of spinal nerves C2-6 |
supplied segmentally by: deep cervical a., posterior intercostal aa. |
splenius means bandage; it gets its name from its broad, flat shape |
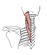 |
| stapedius |
walls of the pyramidal eminence |
neck of the stapes |
dampens vibration of the stapes |
facial nerve (VII) |
anterior tympanic a. |
entirely enclosed in bone, except for its tendon; a derivative of the second
pharyngeal arch |
 |
| sternocleidomastoid |
sternal head: anterior surface of the manubrium; clavicular head: medial
1/3rd of the clavicle |
mastoid process and lateral 1/2 of the superior nuchal line |
draws the mastoid process down toward the same side which causes the chin
to turn up toward the opposite side; acting together, the muscles of the two
sides flex the neck |
spinal accessory nerve (XI), with sensory supply from C2 & C3 (for proprioception) |
sternocleidomastoid branch of the occipital a. |
carotid sheath structures lie deep to it |
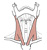 |
| sternohyoid |
posterior surfaces of both the manubrium and sternal end of the clavicle |
lower border of the hyoid bone, medial to the omohyoid m. insertion |
depresses/stabilizes the hyoid bone |
ansa cervicalis |
superior thyroid a. |
sternohyoid overlies the sternothyroid and thyrohyoid mm. |
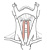 |
| sternothyroid |
posterior surface of the manubrium below the origin of the sternohyoid m. |
oblique line of the thyroid cartilage |
depresses/stabilizes the hyoid bone |
ansa cervicalis |
superior thyroid a. |
sternothyroid lies deep to the sternohyoid m. |
 |
| styloglossus |
anterior side of the styloid process |
posterolateral side of the tongue |
retracts and elevates the tongue |
hypoglossal nerve (XII) |
ascending pharyngeal a., ascending palatine branch of the facial a. |
an extrinsic muscle of the tongue |
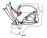 |
| stylohyoid |
posterior side of the styloid process |
splits around the intermediate tendon of the digastric m. to insert on the
body of the hyoid bone |
elevates and retracts the hyoid bone |
facial nerve (VII) |
ascending pharyngeal a. |
facial nerve innervates both the stylohyoid m. and the posterior belly of
the digastric m. shortly after exiting from the stylomastoid foramen |
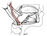 |
| stylopharyngeus |
medial side of the styloid process |
superior border of the thyroid cartilage and also into the pharyngeal wall |
elevates the larynx |
glossopharyngeal nerve (IX) |
ascending pharyngeal a. |
stylopharyngeus, the only muscle innervated by IX, is the only muscle of
the pharyngeal wall NOT innervated by the vagus (X) nerve; it is a derivative
of the third pharyngeal arch |
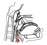 |
| superior oblique |
apex of the orbit above the optic canal |
sclera on the posterior superior surface of the eyeball |
depresses and abducts the eyeball; rotates the superior pole of the iris
medially |
trochlear nerve (IV) |
ophthalmic a. |
passes through a fibrocartilagenous pulley known as the trochlea; when the
eye is adducted, this muscle moves the cornea inferiorly |
 |
| superior pharyngeal constrictor |
medial pterygoid plate, pterygoid hamulus, pterygomandibular raphe, mylohyoid
line of mandible |
pharyngeal tubercle and midline pharyngeal raphe |
constricts the pharyngeal cavity |
vagus (X), via the pharyngeal plexus |
ascending pharyngeal a. |
the most internal of the three pharyngeal constructor mm. |
 |
| superior rectus |
common tendinous ring at the apex of the orbit |
sclera on the superior surface of the eyeball |
elevates and adducts the eyeball; rotates the superior pole of the iris
medially |
oculomotor nerve (III), superior division |
ophthalmic a. |
because this muscle approaches the eye from a medial position, it causes
the iris to rotate medially |
 |
| temporalis |
temporal fossa and the temporal fascia |
coronoid process of the mandible and the anterior surface of the ramus of
the mandible |
elevates the mandible; retracts the mandible (posterior fibers) |
anterior and posterior deep temporal nerves from the mandibular division
of the trigeminal nerve (V) |
anterior and posterior deep temporal aa. |
a powerful chewing muscle; a derivative of the first pharyngeal arch |
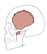 |
| tensor tympani |
cartilagenous auditory tube and the greater wing of the sphenoid bone which
lies adjacent to it |
manubrium of the malleus |
dampens vibrations of the tympanic membrane |
medial pterygoid branch of the mandibular division of the trigeminal nerve
(V) |
superior tympanic branch of the middle meningeal a. |
V3 innervates both tensor muscles of the head (tympani and veli palatini)
which are derivatives of the first pharyngeal arch |
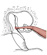 |
| tensor veli palatini |
scaphoid fossa, lateral wall of the auditory tube cartilage |
palatine aponeurosis |
opens the auditory tube; tenses the soft palate |
mandibular division of the trigeminal nerve (V) |
ascending pharyngeal a. |
remember: V3 innervates both tensor muscles (tympani and veli palatini);
ALL other palatal muscles are innervated by vagus |
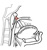 |
| thyroarytenoid |
inner surface of the thyroid cartilage anteriorly |
lateral border of the arytenoid cartilage |
draws the arytenoid cartilage forward, relaxing and adducting the vocal
folds |
inferior laryngeal nerve, from recurrent laryngeal nerve, a branch of the
vagus nerve (X) |
laryngeal branch of the superior thyroid a. |
its subsidiary parts are the thyroepiglottic m. and the vocalis m.; the
medial most fibers of thyroarytenoid that insert along the vocal ligament are
called the vocalis muscle |
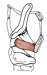 |
| thyroepiglottic |
inner surface of the thyroid cartilage near the laryngeal prominence |
lateral surface of the epiglottic cartilage |
draws the epiglottic cartilage downward |
inferior laryngeal nerve, from recurrent laryngeal nerve, a branch of the
vagus nerve (X) |
laryngeal branch of the superior thyroid a. |
represents the superior fibers of thyroarytenoid muscle which fan out to
the quadrangular membrane and epiglottis |
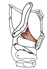 |
| thyrohyoid |
oblique line of the thyroid cartilage |
lower border of the hyoid bone |
elevates the larynx; depresses/stabilizes the hyoid bone |
ansa cervicalis (via fibers running with the hypoglossal nerve that leave
XII distal to the superior limb of ansa) |
superior thyroid a. |
thyrohyoid lies deep to the sternohyoid |
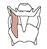 |
| trachealis |
posterior edge of the tracheal cartilage |
posterior edge of the tracheal cartilage of other side (joins tracheal rings
posteriorly) |
constricts the bronchi and trachea |
preganglionic parasympathetic fibers from the vagus (X) nerve |
inferior thyroid a., bronchial aa. |
smooth muscle, found in the submucosal layer |
 |
| transverse arytenoid |
posterior surface of the arytenoid cartilage |
posterior surface of the contralateral arytenoid cartilage |
draws arytenoid cartilages together, adducting the vocal folds |
inferior laryngeal nerve, from recurrent laryngeal nerve, a branch of the
vagus nerve (X) |
laryngeal br. of the superior thyroid a. |
the transverse arytenoid m.lies anterior to the oblique arytenoid m.; the
arytenoideus is often considered to be one muscle with oblique and transverse
parts |
 |
| transverse arytenoid |
posterior surface of the arytenoid cartilage |
posterior surface of the contralateral arytenoid cartilage |
draws arytenoid cartilages together, adducting the vocal folds |
inferior laryngeal nerve, from recurrent laryngeal nerve, a branch of the
vagus nerve (X) |
laryngeal br. of the superior thyroid a. |
the transverse arytenoid m.lies anterior to the oblique arytenoid m.; the
arytenoideus is often considered to be one muscle with oblique and transverse
parts |
 |
| vocalis |
surface of the thyroid cartilage, vocal process of the arytenoid cartilage |
vocal ligament |
relaxes segments of the vocal ligament, thereby adjusting pitch |
inferior laryngeal nerve, from the recurrent laryngeal nerve, a branch of
the vagus nerve (X) |
laryngeal br. of the superior thyroid a. |
represents the innermost fibers of the thyroarytenoid muscle; the cricothyroid
m. grossly tenses the vocal ligaments, while the vocalis muscle provides the
mechanism for fine tuning the vibrations of the vocal folds |
 |
| zygomaticus major |
upper lateral surface of the zygomatic bone |
skin of the angle of the mouth |
elevates and draws the corner of the mouth laterally |
zygomatic and buccal branches of the facial nerve (VII) |
transverse facial a., facial a. |
a "smile" muscle |
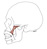 |
| zygomaticus minor |
lower surface of the zygomatic bone |
lateral part of the upper lip |
elevates the upper lip |
buccal branch of the facial nerve (VII) |
transverse facial a., facial a. |
a "smile" muscle |
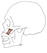 |

