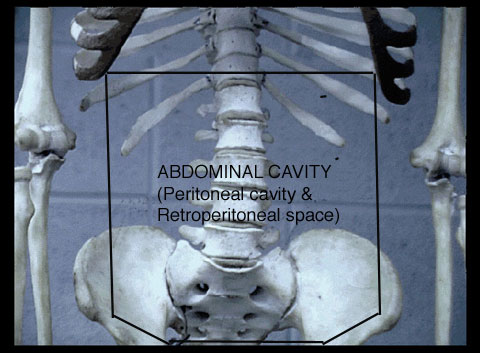
The abdominal cavity is bounded above by the thoraco-abdominal diaphragm (the respiratory diaphragm or "THE" diaphragm) and below by the pelvic inlet. It is continuous through the pelvic inlet with the pelvic cavity, and the combined space is the abdominopelvic cavity. The abdominal cavity contains the peritoneal cavity, the abdominal organs, and the retroperitoneal space.
The peritoneal cavity is a potential space between the parietal peritoneum lining the body wall and visceral peritoneum covering the abdominal organs. The peritoneal cavity is a serous sac, similar to the pleural and pericardial cavities. The retroperitoneal space is behind the peritoneum of the posterior abdominal wall. |