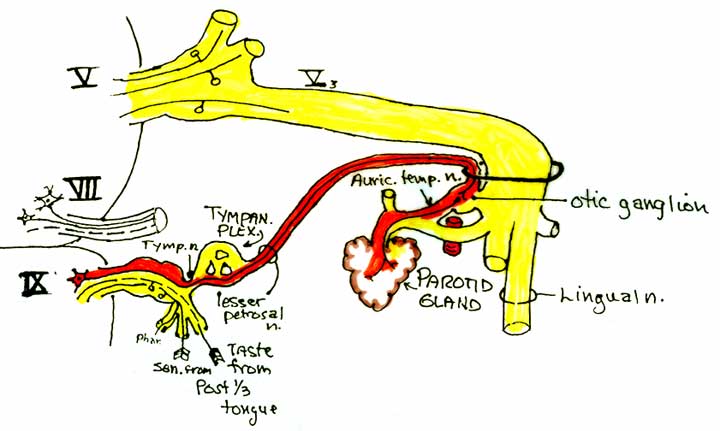
The otic ganglion story - until the synapse happens
As the glossopharyngeal nerve (IX) passes inferiorly through the jugular foramen, it gives off a tympanic branch, carrying preganglionic parasympathetic fibers, that passes upward through the inferior tympanic canaliculus to pass into the middle ear. There, it forms a tympanic plexus on the promontory, an eminence on the medial wall of the middle ear cavity. Stretching anteromedially from the promontory, and piercing the anterior wall of the middle ear cavity, is the lesser petrosal nerve. Lesser petrosal nerve travels anteromedial on the anterior surface of the petrous temporal bone, just lateral to the greater petrosal nerve (more on that one later). Lesser petrosal passes inferiorly through the skull base, usually through foramen ovale. Immediately below the skull, it passes into the otic ganglion, located on the medial surface of the mandibular division of trigeminal nerve (V3) below its exit through foramen ovale. And, to paraphrase a bumper sticker, synapse happens.
|