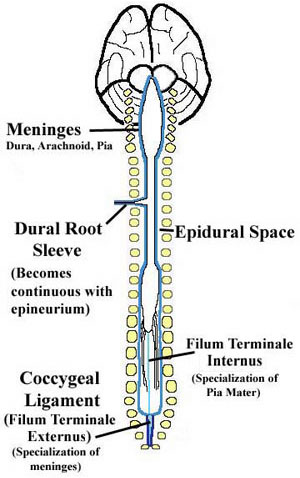 
The spinal cord is further protected by three membranes, collectively called the meninges. The outer membrane surrounding the spinal cord is the dura mater (from Latin, meaning durable mother). The dura, made of a dense fibrous material, forms the dural sac, which surrounds the spinal cord and cauda equina (to be discussed later) and terminates at the level of the second sacral vertebra. The dura is separated from the vertebrae by the epidural fat in the epidural space (epi, meaning upon). The next layer is the delicate arachnoid mater which is thin and has web-like filaments connecting to the underlying pia mater (arachnoid is Greek for spider). Beneath the arachnoid mater is the subarachnoid space, which is filled with cerebrospinal fluid. Abbreviated CSF, cerebrospinal fluid bathes the brain and spinal cord as well as the cauda equina, providing protection, nourishment, and a medium for exchange of nutrients and waste. The innermost membrane surrounding the spinal cord is the vascular pia mater (Latin, meaning tender or devoted mother), which is very closely apposed to the spinal cord. The pia mater has paired specializations called denticulate ligaments, which extend laterally from the surface of the spinal cord and pierce the arachnoid to attach to the inner aspect of the dura mater at 21 pairs of denticulations (dentate means tooth-like - these are tooth-like lateral projections). The denticulate ligaments run longitudinally between the dorsal and ventral roots of the spinal cord and serve to suspend the spinal cord from side to side in the dural sac. The pia continues inferiorly from the end of the spinal cord (at the level of the second lumbar vertebra) as the filum terminale internum. As we said, the dural sac ends at the level of the second sacral vertebra (S2). Caudal to the end of the dural sac is a specialization of meninges called the coccygeal ligament (or filum terminale externum) that attaches the meninges, and consequently the spinal cord, to the coccyx. The coccygeal ligament is composed of specializations of all three layers of meninges. |







