| The parasympathetic and sympathetic components of the autonomic nervous system (ANS) differ in their structure and in their function, but the two systems have some important features in common. Both the parasympathetic and sympathetic divisions are two-neuron systems with the first neuron named either presynaptic or preganglionic (these terms are synonymous), and the second nerve called postsynaptic or postganglionic. |
 |
|
It is important to realize that an autonomic neuron is not called postsynaptic or postganglionic until it has synapsed, regardless of how many ganglia it has passed through. The cell bodies of the presynaptic neurons of both the parasympathetic and sympathetic systems are located within the central nervous system. These presynaptic autonomic neurons synapse only with postsynaptic autonomic neurons. (There is one exception, in the adrenal gland, which will be discussed later in this module.) The cell bodies of postsynaptic autonomic neurons are located in ganglia throughout the body. Recall that a ganglion is simply a collection of neuron cell bodies in the peripheral nervous system. Sensory ganglia, such as dorsal root ganglia, are collections of sensory neuron cell bodies, but NO synapses occur there. A particular autonomic ganglion will be associated with synapses of either the parasympathetic nervous system or the sympathetic nervous system, but it may have fibers from both systems running through it. Remember, a neuron does not necessarily synapse just because it enters a ganglion. Some fibers pass through without synapsing. (The terms preganglionic and postganglionic may be a bit deceptive, but they are often used instead of presynaptic and postsynaptic.) Another important similarity between the parasympathetic and sympathetic divisions of the ANS is that they both use chemical signals to alter the action of the organs they innervate. The organs innervated by the autonomic nervous system are called effector organs.
|
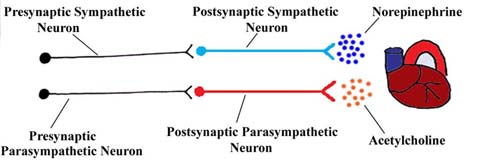 |
| The significant differences between the parasympathetic and sympathetic nervous systems include the location of the presynaptic nerve cell bodies within the central nervous system, and the location of the postsynaptic nerve cell bodies throughout the body. We will discuss the pre- and postsynaptic neurons in detail in this module. Another important difference between the parasympathetic nervous system and the sympathetic nervous system are the neurotransmitters each system uses to effect change. Generally, the sympathetic nervous system releases a chemical called norepinephrine, which is excitatory to neurons, from its postsynaptic neurons. The parasympathetic nervous system releases a chemical called acetylcholine from its postsynaptic neurons.
|







