|
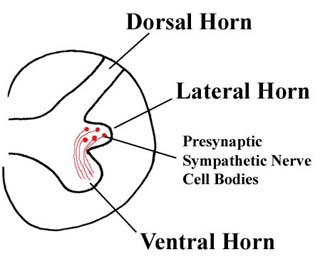
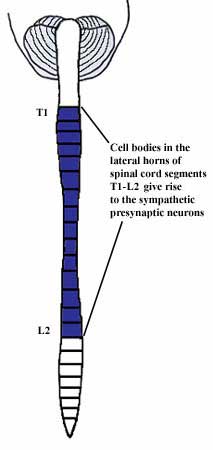
We will first spend some time discussing the sympathetic division of the autonomic nervous system. The sympathetic division is sometimes called the thoracolumbar outflow or division of the ANS because the cell bodies of the presynaptic sympathetic neurons are located in the lateral horns (a.k.a. intermediolateral cell columns) of the spinal cord gray matter, which are found in spinal cord segments T1 through L2. There are no sympathetic presynaptic cell bodies above spinal cord level T1 or below spinal cord level L2. The cell bodies of the postsynaptic sympathetic neurons are found in either paravertebral or prevertebral ganglia. The paravertebral ("beside the vertebrae") ganglia are called the sympathetic chain ganglia and will be discussed in more detail later. Prevertebral ganglia, also known as preaortic or collateral ganglia, are located around the major branches of the abdominal aorta and include the celiac, aorticorenal, superior mesenteric, and inferior mesenteric ganglia. The sympathetic nervous system innervates essentially all the organs of the body as well as blood vessels (smooth muscle in vessel walls), sweat glands, and arrector pili muscles through out the body. (Arrector pili muscles make the hairs on your body stand up, resulting in goose bumps.) |
|