

|
|
||||||||||||
Anatomy Tables - Joints of the Upper & Lower Limbs |
|||||||||||||
Osteology |
||
|---|---|---|
| Bone | Structure | Description |
| os coxae (pelvic or innominate bone) (N486,TG3-04,TG3-05) |
three fused bones: ischium, ilium & pubis | |
| acetabulum | socket for head of femur (Latin, acetabulum = a shallow wide-mouthed vessel or cup) | |
| acetabular notch | notch in the inferior margin of the acetabulum | |
| lunate surface of acetabulum | smooth articular surface within the acetabulum | |
| obturator foramen | large foramen surrounded by the superior and inferior pubic rami, the ischial ramus and the acetabulum; obturator means to occlude or stop up, a reference to the fact that the obturator membrane closes the obturator foramen almost completely; a site of attachment for the obturator externus m. and the obturator internus m. | |
| femur (N489,TG3-06,TG3-07) |
(Latin, femur = thigh) | |
| body | long cylindrical central part of femur; also known as: shaft | |
| head | smooth, rounded proximal end; articulates with acetabulum | |
| fovea capitis femoris | pit in the femoral head; attachment site of ligamentum capitis femoris (Latin, fovea = a pit + capitis = head) | |
| neck | constricted area distal to head | |
| intertrochanteric line | on anterior surface; ridge coursing between greater and lesser trochanters | |
| intertrochanteric crest | on posterior surface; heavy ridge coursing between greater and lesser trochanters | |
| medial condyle | located at distal end; articulates with medial condyle of tibia (Greek, kondyle = the knob formed by the knuckle of any joint) | |
| lateral condyle | located at distal end; articulates with lateral condyle of tibia (Greek, kondyle = the knob formed by the knuckle of any joint) | |
| intercondylar fossa | between the condyles at distal end; accommodates cruciate ligaments | |
| patellar surface | the smooth anterior surface at the inferior end of the femur; it articulates with the posterior surface the patella | |
| patella (TG3-06) |
a sesamoid bone in the quadriceps femoris tendon; articulates with anterior surface of inferior femur | |
| tibia (N513,TG3-08,TG3-09) |
||
| medial condyle | at proximal end; articulates with medial condyle of femur; larger than lateral condyle (Greek, kondyle = the knob formed by the knuckle of any joint) | |
| lateral condyle | at proximal end; articulates with lateral condyle of femur; smaller than medial condyle (Greek, kondyle = the knob formed by the knuckle of any joint) | |
| intercondylar eminence | projection between condyles; attachment site of cruciate ligaments & medial & lateral meninsci (Greek, kondyle = the knob formed by the knuckle of any joint) | |
Joints - Pectoral Girdle & Shoulder |
||
|---|---|---|
| Joint | Description | Significance |
| sternoclavicular joint (N419,TG2-42A, TG2-42BC) |
the joint what connects the clavicle with the sternum | a synovial joint; its joint capsule is subdivided by a fibrous articular disc; it is strengthened by the sternoclavicular, interclavicular and costoclavicular ligaments; the sternoclavicular joint has the range of movement, but not the form, of a ball and socket joint |
| acromioclavicular joint (N423,TG2-42) |
the joint between the distal end of the clavicle and the acromion of the scapula | a plane synovial joint; the shape of the articulation encourages the acromion to slide inferior to the clavicle during dislocation (shoulder separation) a condition that occurs when the coracoclavicular ligament is torn; a small articular disk occurs within this joint capsule |
| articular disc of sternoclavicular joint (TG2-42BC) |
fibrocartilage | serves as a shock absorber of forces transmitted along the clavicle from the upper limb and divides the SC joint into two compartments |
| coracoclavicular ligament (N423,TG2-42) |
syndesmosis | connects upper surface of coracoid process to under surface of clavicle; often subdivided into conoid (posteromedial) & trapezoid ligaments |
| coracoacromial ligament (N423,TG2-42) |
syndesmosis | connects coracoid process with acromion; passes superior to humeral head & supraspinatus tendon |
| transverse scapular ligament, superior (TG2-42A) |
syndesmosis | passes across scapular notch, converting it into a foramen containing suprascapular nerve |
| sternoclavicular ligament (N419,TG2-42A) |
capsular ligament | connects clavicle with sternum; described as separate anterior & posterior ligaments |
| glenohumeral ligament, inferior (N423,TG2-42A,TG2-42BC) |
capsular ligament | connects humerus to scapula; represents an anteroinferior thickening of the shoulder joint capsule |
| glenohumeral ligament, middle (N423,TG2-42A,TG2-42BC) |
capsular ligament | connects humerus to scapula; represents an anterointermediate thickening of the shoulder joint capsule |
| glenohumeral ligament, superior (N423,TG2-42A,TG2-42BC) |
capsular ligament | connects humerus to scapula; represents an anterosuperior thickening of the shoulder joint capsule |
| glenoid labrum (N423,TG2-42A,TG2-42BC) |
fibrocartilage | a part of the glenohumeral joint (Greek, glene = a shallow socket + eidos = appearence) |
| shoulder joint (N423,TG2-42A,TG2-42BC) |
synovial, ball & socket, diarthrosis | connects humerus & scapula; glenoid labrum deepens the socket, glenohumeral ligaments/bands add strength anteriorly; tendon of long head of biceps passes through shoulder joint |
| subscapular bursa (N423,TG2-42A,TG2-42BC) |
extension of glenohumeral cavity | protects the subscapular tendon where it passes inferior to the coracoid process and over the scapular neck |
| tendon of the long head of the biceps (N423,TG2-42A,TG2-42BC) |
tendon enlosed by a synovial sheath | moves back and forth in the intertubercular groove of the humerus |
| transverse humeral ligament (N423,TG2-42A,TG2-42BC) |
syndesmosis | passes from the lesser to greater tubercle and holds the tendon of the long head of the biceps in the intertubercular groove |
Joints - Elbow & Wrist |
||
|---|---|---|
| Joint | Description | Significance |
| elbow joint (N436,TG2-43A,TG2-43BC) |
synovial; hinge (gingylmus), gliding and pivot | complex joint consisting of humeroulnar, humeroradial and proximal radioulnar articulations; strengthened primarily by radial & ulnar collateral ligaments |
| radial collateral ligament, elbow (N438,TG2-43BC) |
lateral fanlike ligament | extends from the lateral epicondyle of the humerus and blends distally with the anular ligament of the radius |
| ulnar collateral ligament, elbow (N438,TG2-43BC) |
anterior band - strong posterior - fanlike, weak oblique - slender, deepens the socket for the trochlea of the humerus |
extends from the medial epicondyle of the humerus to the coronoid process and olecranon of the ulna (Latin, ulna = elbow) |
| radioulnar joint, proximal (N438,TG2-43BC) |
synovial, pivot | connects radial head with ulna; annular ligament holds radial head against radial notch of ulna (Latin, ulna = elbow) |
| annular ligament (N438,TG2-43BC) |
the ligament that encircles the head of the radius | it forms 4/5 of a circle - the radial notch of the ulna forms the other 1/5; it attaches to the margins of the radial notch; it holds the head of the radius against the ulna and cups in distal to the head to provide restraint against distal dislocation of the radius (Latin, anulus = ring) |
| radioulnar joint, intermediate (N439, TG2-21) |
syndesmosis | interosseous membrane connects radius to ulna; forces transferred from radius to ulna |
| interosseous membrane, forearm (N439,TG2-21) |
a fibrous membrane that connects the interosseous borders located on the shafts of the radius and the ulna | a syndesmosis; its fibers are oriented obliquely downward from the radius toward the ulna; the interosseous membrane is the classic example of a syndesmosis; proximally directed forces from the hand pass through the radius and are transferred to the ulna through the interosseous membrane; marked proximally by the oblique cord |
| radioulnar joint, distal (N454,N455,TG2-44A,TG2-44B) |
synovial, pivot | characterized by an intracapsular articular disk (Latin, ulna = elbow) |
| radiocarpal (wrist) joint (N454, N455,TG2-44A,TG2-44B) |
synovial, ellipsoidal | characterized by an intracapsular articular disk; radius articulates with the proximal row of carpals |
| radial collateral ligament, wrist (N454, N455,TG2-44A,TG2-44B) |
it connects the styloid process of the radius with the scaphoid and trapezium | it reinforces the articular capsule on the lateral side of the wrist |
| ulnar collateral ligament, wrist (N454, N455,TG2-44A, TG2-44B) |
it connects the styloid process of the ulna to the pisiform and triquetrum | it reinforces the articular capsule on the medial side of the wrist (Latin, ulna = elbow) |
| distal radioulnar articulation (TG2-44C) |
synovial, pivot | the rounded head of the ulna articulates with the ulnar notch on the medial distal end of the radius |
| dorsal radiocarpal ligament (N455, TG2-44) |
capsular ligament | allows the hand to follow the radius during pronation of the forearm |
| palmar radiocarpal ligament (N454,TG2-44) |
capsular ligament | allows the hand to follow the radius during supination of the forearm |
Joints - Hand |
||
|---|---|---|
| Joint | Description | Significance |
| midcarpal joint (N455,TG2-44) |
synovial, ball & socket | the joint between the proximal and distal rows of carpal bones; assists in flexion and extension at wrist |
| intermetacarpal articulation (N455,TG2-44) |
synovial, plane | the metacarpals articulate with each other at their bases |
| carpometacarpal articulation (N455,TG2-44) |
synovial, saddle (thumb) | the CMC joint of the thumb is located between the trapezium and the base of the 1st metacarpal and has a separate joint cavity |
| carpometacarpal joint, thumb (N455,TG2-44) |
synovial, saddle (concavoconvex) | connects trapezium with metacarpal of thumb; flexion/extension, abduction/adduction |
| carpometacarpal joints, fingers (N455,TG2-44) |
synovial, plane | connects distal carpal bones with metacarpals of fingers; tightly bound by ligaments to limit motion |
| metacarpophalangeal joints (N458,TG2-45) |
synovial, condyloid or ellipsoid | connects metacarpal head to base of proximal phalanx; strengthened by collateral ligaments; heads of metacarpals are firmly joined by transverse metcarpal ligaments to provide a stable platform for finger movements |
| transverse metacarpal ligament, deep (N458,TG2-45) |
a ligament that connects the metacarpophalangeal joints 2-5 on their palmar surface | limited motion is permitted between the distal ends of adjacent metacarpal bones due to the presence of the deep transverse metacarpal ligaments; the metacarpal bones are bound together to form a solid foundation for finger movements |
| interphalangeal joints (N458,TG2-45) |
synovial, hinge | connect proximal & middle phalanges (proximal interphalangeal joint) and middle & distal phalanges (distal interphalangeal joint); strengthened by collateral ligaments |
Joints - Hip |
||
|---|---|---|
| Joint | Description | Significance |
| acetabular labrum (N487,TG3-55) |
fibrocartilage | fibrocartilage forming rim of acetabulum; deepens the acetabulum (Latin, acetabulum = a shallow wide-mouthed vessel or cup + labrum = lip) |
| transverse acetabular ligament (N487,TG3-55) |
bridges the acetabular notch; forms a bridge over the artery in the ligament of the femoral head (ligamentum capitis femoris) (Latin, acetabulum = a shallow vessel or cup) | |
| ligamentum capitis femoris (N487,TG3-55) |
intracapsular ligament connecting transverse acetabular ligament with fovea capitis femoris; also known as: ligament of the femoral head (Latin, capitis = head) | |
| zona orbicularis (TG3-55A,TG3-55B) |
fibrous | capsular fibers fromthe hip bone to the intertrochanteric line, forming a collar to help hold the femoral head in place |
| pubofemoral ligament (N487,TG3-54) |
capsular ligament of hip joint connecting superior pubic ramus to medial surface of femoral neck | |
| iliofemoral ligament (N487,TG3-54) |
capsular ligament of the hip joint connecting anterior inferior iliac spine to intertrochanteric line | |
| ischiofemoral ligament (N487,TG3-54) |
capsular ligament of the hip joint connecting body of ischium to posterior femoral neck (Latin, ischion = hip joint) | |
| hip joint (N487,TG3-54) |
synovial | acetabulum of os coxae articulates with femoral head; reinforced by capsular ligaments (iliofemoral, pubofemoral, ischiofemoral, zona orbicularis) and containing acetabular labrum & ligamentum capitis femoris |
| iliopectineal bursa (N487,N496,TG3-54) |
bursa | lies deep to the iliopsoas tendon as it crosses the neck of the femur and the capsule of the hip joint |
Joints - Knee |
||
|---|---|---|
| Joint | Description | Significance |
| infrapatellar synovial fat pads (N507,N511,TG3-58) |
synovial | masses of loose fatty tissue on both sides of the patellar ligament |
| knee joint (N507,N509,TG3-57,TG3-58,TG3-59) |
synovial | femoral condyles articulate with tibial condyles; reinforced by intracapsular ligaments (anterior cruciate & posterior cruciate), a capsular ligament (tibial collateral ligament), and an extracapsular ligament (fibular collateral ligament); contains medial & lateral menisci |
| patellar ligament (N511,TG3-57) |
tendon | connects quadriceps femoris muscle group to the tibial tuberosity; patella is a sesamoid bone within the quadriceps tendon |
| tibial collateral ligament (N507,N509,TG3-57,TG3-58,TG3-59) |
capsular ligament of the knee joint connecting medial epicondyle of femur with medial surface of medial tibial condyle; its attachment to the medial meniscus is clinically relevant | |
| fibular collateral ligament (N507,N509,TG3-57,TG3-58,TG3-59) |
extracapsular ligament, not part of the fibrous capsule of the knee; connects lateral epicondyle of femur with fibular head | |
| anterior cruciate ligament (N507, N509,TG3-58,TG3-59) |
intracapsular ligament connecting anterior aspect of intercondylar eminence of tibia with medial surface of lateral femoral condyle | |
| posterior cruciate ligament (N507,N509,TG3-58,TG3-59) |
intracapsular ligament connecting posterior aspect of intercondylar eminence of tibia with lateral surface of medial femoral condyle | |
| medial meniscus (N507,N509,TG3-58,TG3-59) |
fibrocartilage | C-shaped intra-articular disc within knee joint between medial femoral condyle & medial tibial condyle; attached to tibial collateral ligament, coronary ligament, & intercondylar eminence (Greek, meniskos = crescent) |
| lateral meniscus (N507,N509,TG3-58,TG3-59) |
fibrocartilage | C-shaped intra-articular disc within knee joint between lateral femoral condyle & lateral tibial condyle; attached to coronary ligament & intercondylar eminence (Greek, meniskos = crescent) |
| posterior meniscofemoral ligament (TG3-59) |
intracapsular ligament connects posterior part of lateral meniscus with lateral surface of medial femoral condyle | |
| suprapatellar bursa (N507,TG3-58) |
bursa | superior extension of the synovial membrane of the knee joint; passes deep to the quadriceps tendon |
| prepatellar bursa (N511) |
bursa | subcutaneous bursa overlying patella |
| infrapatellar bursa, superficial (N511) |
bursa | subcutaneous bursa overlying patellar tendon |
| infrapatellar bursa, deep (N511) |
bursa | bursa lying between patellar tendon & tibia |
Joints - Ankle |
||
|---|---|---|
| Joint | Description | Significance |
| interosseous membrane of the leg (N514,TG3-30) |
syndesmosis | the membrane that connects the interosseous borders of the shafts of the tibia and fibula |
| distal tibiofibular joint (N514,TG3-60A,TG3-60B) |
syndesmosis | tibia and fibula are bound together by anterior, posterior, and transverse tibiofibular ligaments |
| ankle joint (N514,TG3-60A,TG3-60B) |
synovial, hinge | articulation between distal end of tibia, medial malleolus, lateral malleolus and talus; reinforced by deltoid ligament (anterior tibiotalar, tibionavicular, tibiocalcaneal, posterior tibiotalar), anterior talofibular, calcaneofibular & posterior talofibular ligaments |
| anterior tibiofibular ligament (N514,TG3-60A,TG3-60B) |
connects distal ends of tibia & fibula anteriorly | |
| posterior tibiofibular ligament (N514,TG3-60A,TG3-60B) |
connects distal ends of tibia & fibula posteriorly | |
| transverse inferior tibiofibular ligament N514) | forms a strong connection between the distal ends of the tibia and fibula | |
| deltoid ligament (N527,TG3-60) |
connects medial malleolus with talus, navicular & calcaneus; its four parts arranged from anterior to posterior: anterior tibiotalar, tibionavicular, tibiocalcaneal, posterior tibiotalar; also known as: medial ligament of ankle | |
| anterior tibiotalar ligament (N527,TG3-60) |
part of deltoid ligament connecting medial malleolus with talus | |
| posterior tibiotalar ligament (N527,TG3-60) |
part of deltoid ligament connecting medial malleolus with talus posteriorly | |
| tibiocalcaneal ligament (N527,TG3-60) |
part of deltoid ligament connecting medial malleolus with sustentaculum tali | |
| tibionavicular ligament (N527,TG3-60) |
part of deltoid ligament connecting medial malleolus with navicular | |
| anterior talofibular ligament (N527,TG3-60) |
connects lateral malleolus with talus anterolaterally | |
| posterior talofibular ligament (N527,TG3-60) |
connects lateral malleolus with talus posterolaterally | |
| calcaneofibular ligament (N527,TG3-60) |
connects lateral malleolus with calcaneus | |
Joints - Foot |
||
|---|---|---|
| Joint | Description | Significance |
| plantar calcaneonavicular ligament (N528,TG3-61) |
syndesmosis | connects sustentaculum tali with inferior surface of navicular; also known as: spring ligament |
| subtalar joint (N524,N525,TG3-41,TG3-60) |
synovial | articulation between talus and calcaneous, strengthened by the interosseous talocalcaneal ligament |
| interosseous talocalcaneal ligament (N524,N525,TG3-60) |
syndesmosis | connects the neck of the talus with calcaneus, filling the tarsal sinus(Latin, inter = between + os = bone) |
| transverse tarsal joint (N523,TG3-61) |
synovial | two joints in line, talonavicular and calcaneocuboid, allow most inversion/eversion to happen through this joint |
| plantar calcaneocuboid (short plantar) ligament (N528,TG3-61) |
syndesmosis | connects calcaneus & cuboid inferiorly |
| long plantar ligament (N528,TG3-61) |
syndesmosis | connects calcaneus with cuboid & bases of lateral 3 metatarsals |
| tarsometatarsal joints (N523,TG3-61) |
synovial | reinforced by dorsal & plantar ligaments |
| metatarsophalangeal joints (5) (N523,TG3-61) |
synovial | condyloid joint connecting head of metatarsal with proximal phalanx; reinforced by collateral ligaments |
| longitudinal arch of the foot (TG3-41) |
combination of synovial joints & syndesmoses | passes from calcaneus to talus to navicular to cuneiforms to metatarsals; supported by plantar calcaneonavicular ligament & many other ligaments; supported by tendons of tibialis anterior & tibialis posterior mm. |
| transverse arch of the foot (TG3-41) |
combination of synovial joints & syndesmoses | passes through distal row of tarsal bones; supported by shape of bones and many ligaments; supported by tendons of fibularis longus & tibialis anterior & tibialis posterior mm. |
Muscles |
|||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Muscle | Origin | Insertion | Action | Innervation | Blood Supply | Notes | Image |
| obturator externus (N493, N539,TG3-21,TG3-64) |
the external surface of the obturator membrane and the superior and inferior pubic rami | trochanteric fossa of the femur | laterally rotates the thigh | obturator nerve | obturator a. | the tendon of the obturator externus m. passes inferior to the neck of the femur to reach its insertion site | 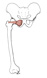 |
Arteries |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Artery | Source | Branches | Supply to | Notes |
| obturator (N487,TG3-55) |
internal iliac a., anterior division | pubic br., acetabular br., anterior br., posterior br. | medial thigh and hip | anterior and posterior brs. pass on the anterior and posterior sides of the adductor brevis m.; aberrant obturator a. arises from the inferior epigastric a. in 30% of cases |
| The material presented in these tables is contained in the book: MedCharts Anatomy by Thomas R. Gest & Jaye Schlesinger Published by ILOC, Inc., New York Copyright © 1995, unauthorized use prohibited. |
The excellent editorial assistance of Dr. Pat Tank, UAMS is gratefully acknowledged. |