

|
|
||||||||||||
Anatomy Tables - Anterior & Lateral Leg & Foot |
|||||||||||||
Osteology |
|||
|---|---|---|---|
| Bone | Structure | Description | Notes |
| tarsal bones (N523, N524,TG3-40A,TG3-40B) |
the bones of the ankle | there are seven tarsal bones: talus, calcaneus, navicular, medial cuneiform, intermediate cuneiform, lateral cuneiform, cuboid | |
| transverse tarsal joint (N523,TG3-61) |
formed by the combined talonavicular part of the talocalcaneonavicular and calcaneocuboid joints | synovial joint responsible for inversion/eversion of the foot; transection across this joint is a standard method for surgical amputation of the foot | |
| talus (N523,TG3-40) |
the most proximal of the tarsal bones | the talus articulates with the medial malleolus of the tibia and the lateral malleolus of the fibula to form the ankle mortise joint (Latin, talus = ankle bone) | |
| body | the proximal part of the talus | its superior (trochlear) part participates in the ankle joint and its inferior part articulates with the calcaneus | |
| subtalar joint (N524, N525,TG3-41A,TG3-41B) |
occurs where the talus rests on and articulates with the calcaneus | ||
| trochlea | the superior portion of the body of the talus that lies between the two malleoli | it has a smooth articular surface; it participates in the formation of the ankle joint (Latin, trochlea = pulley) | |
| head | the portion of the talus that projects anteriorly | it articulates with the navicular bone | |
| neck | the constricted part of the talus located proximal to the head | ||
| calcaneus (N525,TG3-40A,TG3-40B,TG3-41A,TG3-41B) |
the tarsal bone which forms the heel | it is the largest and strongest bone in the foot; a fracture of the calcaneus which separates the tuberosity from the body can be a debilitating injury (Latin, calcis = heel) | |
| calcaneal tuberosity | the inferior roughened area of the calcaneus which contacts the ground during weight-bearing | it is the attachment site of the plantar aponeurosis, abductor digiti minimi, flexor digitorum brevis, and the long plantar ligament | |
| sustentaculum tali | the shelf-like medial projection of bone located inferior to the medial malleolus | it is a shelf of bone that articulates with and supports the talus; it is grooved inferiorly by the tendon of the flexor hallucis longus m. (Latin, sustento = to hold upright) | |
| navicular (N523,TG3-40) |
the tarsal bone located distal to the talus and proximal to the three cuneiform bones | it articulates with the head of the talus and all three cuneiform bones; it is the attachment site for an important ligament (plantar calcaneonavicular or "spring" ligament) that supports the medial longitudinal arch of the foot (Latin, navicular = small boat shaped structure) | |
| cuneiform, medial (N523,TG3-40) |
the most medial bone in the distal row of tarsal bones | the cuneiform bones articulate with the navicular bone proximally and the bases of the metatarsal bones distally | |
| cuneiform, middle (N523,TG3-40) |
the intermediate bone of the three cuneiform bones | the cuneiform bones articulate with the navicular bone proximally and the bases of the metatarsal bones distally | |
| cuneiform, lateral (N523,TG3-40) |
the bone that is located between the middle cuneiform and the cuboid bone | the cuneiform bones articulate with the navicular bone proximally and the bases of the metatarsal bones distally | |
| cuboid N523,TG3-40) |
the most lateral bone in the distal row of tarsal bones | the cuboid bone articulates with the calcaneus proximally and the fourth and fifth metatarsal bones distally | |
| metatarsals (N524,TG3-40A,TG3-40B) |
the bones located between the tarsal bones and the phalanges | there are five metatarsal bones in the foot | |
| base | the proximal end of the metatarsal | it articulates with the distal row of tarsal bones | |
| body | the slender shaft of the metatarsal | it is also known as the diaphysis | |
| head | the rounded distal end of the metatarsal | it articulates with the proximal phalanx of the corresponding digit | |
| phalanx (phalanges) (N524,TG3-40A,TG3-40B) |
the distal two or three bones in the digits of the foot | there are a total of 14 phalanges in the foot; the great toe has two phalanges (proximal and distal) and each of the other four toes has three phalanges (proximal, middle and distal); (Latin, phalanx = line of soldiers) | |
| base | the proximal end of the phalanx | the base of the proximal phalanx articulates with the head of the corresponding metatarsal bone; the base of the middle or distal phalanx articulates with the head of the next most proximal phalanx | |
| body | the slender shaft of the phalanx | also known as the diaphysis; the body of the distal phalanx is very short | |
| head | the distal end of the phalanx | the proximal, middle and distal phalanges each have a head; the head of a proximal or middle phalanx articulates with the base of the next most distal phalanx | |
Muscles |
|||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Muscle | Origin | Insertion | Action | Innervation | Blood Supply | Notes | Image |
| abductor hallucis (N533,TG3-49) |
medial side of tuberosity of calcaneus | medial side of base of proximal phalanx of hallux | abducts hallux; flexes metatarsophalageal joint | medial plantar nerve | medial and lateral plantar aa. | (Latin, hallex = great toe) | 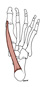 |
| adductor hallucis (N535,TG3-51) |
oblique head: bases of metatarsals 2-4; transverse head: heads of metatarsals 3-5 | lateral side of base of proximal phalanx of hallux | adducts great toe (moves it toward midline of foot; i.e. 2nd digit) | deep branch of lateral plantar nerve | lateral plantar a. | (Latin, hallex = great toe) | 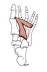 |
| flexor hallucis brevis (N533, N535,TG3-49,TG3-51) |
cuboid, lateral cuneiform, medial side of first metatarsal | medial belly: medial side of proximal phalanx of hallux; lateral belly: lateral side of proximal phalanx | flexes metatarsophalangeal joint of hallux | medial plantar nerve (lateral belly occasionally receives innervation from lateral plantar nerve) | medial and lateral plantar aa. | each tendon of insertion contains a sesamoid bone (Latin, hallex = great toe) | 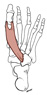 |
| flexor digitorum brevis (N533,TG3-49) |
tuberosity of calcaneus, plantar aponeurosis, intermuscular septa | base of middle phalanx of digits 2-5 after splitting to allow passage of flexor digitorum longus tendons | flexes metatarsophalangeal & proximal interphalangeal joints of digits 2-5 | medial plantar nerve | medial and lateral plantar aa. | 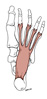 |
|
| fibularis (peroneus) longus (N519, N521,TG3-36,TG3-37) |
upper two/thirds of lateral surface of fibula | after crossing plantar surface of foot deep to intrinsic muscles, it inserts on medial cuneiform and base of 1st metatarsal | plantarflexes and everts the foot | superficial fibular (peroneal) nerve | fibular a. | lies superficial to fibularis brevis m. | 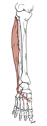 |
| fibularis (peroneus) brevis (N519, N521,TG3-36,TG3-37) |
lower one third of lateral surface of fibula | tuberosity of base of 5th metatarsal | plantarflexes and everts the foot | superficial fibular (peroneal) nerve | fibular a. | 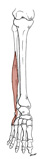 |
|
| tibialis anterior (N519,TG3-37) |
lateral tibial condyle and upper lateral surface of tibia | medial surface of medial cuneiform and 1st metatarsal | dorsiflexes and inverts foot | deep fibular (peroneal) nerve | anterior tibial a. | acts as both an antagonist and a synergist of tibialis posterior | 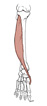 |
| peroneus mm. (SEE fibularis mm.) | peroneus is the old terminology used for fibularis mm. | ||||||
| extensor hallucis longus (N519,TG3-37) |
middle half of anterior surface of fibula & interosseous membrane | base of distal phalanx of hallux | extends metatarsophalangeal & interphalangeal joints of hallux | deep fibular (peroneal) nerve | anterior tibial a. | (Latin, hallex = great toe) | 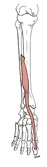 |
| extensor hallucis brevis (N530,TG3-45) |
superolateral surface of calcaneus | dorsum of base of proximal phalanx of hallux | extends great toe | deep fibular (peroneal) nerve | anterior tibial a. | often considered medial-most part of extensor digitorum brevis m. (Latin, hallex = great toe) | 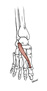 |
| extensor digitorum longus (N519,TG3-37) |
lateral condyle of tibia, anterior surface of fibula, lateral portion of interosseous membrane | dorsum of lateral 4 toes via extensor expansions (central slip inserts on base of middle phalanx, lateral slips on base of distal phalanx) | extends metatarsophalangeal, proximal interphalangeal and distal interphalangeal joints of lateral 4 toes | deep fibular (peroneal) nerve | anterior tibial a. | 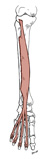 |
|
| extensor digitorum brevis (N530,TG3-45) |
superolateral surface of calcaneus | extensor expansion of toes 2-4 (tendon to hallux is called extensor hallucis brevis) | extends toes 2-4 | deep fibular (peroneal) nerve | dorsalis pedis a. | 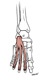 |
|
| fibularis (peroneus) tertius (N521, N530,TG3-37,TG3-45) |
distal part of anterior surface of fibula | dorsum of shaft of 5th metatarsal bone | dorsiflexes and everts foot | deep fibular (peroneal) nerve | anterior tibial a. | fibularis tertius is in the anterior compartment of the leg, not the lateral compartment (which contains fibularis longus and brevis) | 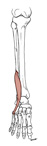 |
| quadratus plantae (N534,TG3-50) |
anterior portion of calcaneus & long plantar ligament | tendons of flexor digitorum longus m. | assists flexor digitorum longus in flexing toes | lateral plantar nerve | lateral plantar a. | (Latin, quadratus = square) | 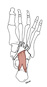 |
| dorsal interosseous, of foot (N531, N535, N536, N537,TG3-46,TG3-51,TG3-52) |
four muscles, from shafts of adjacent metatarsal bones | bases of proximal phalanges for digit 2 (both sides) & digits 3,4 (lateral side) | abduct digits 2-4 (move these digits away from midline as defined by a line passing through 2nd digit), flex metatarsophalangeal joints and extend interphalangeal joints of those digits | deep branch of lateral plantar nerve | arcuate a.; deep plantar a. | remember DAB (dorsal interossei ABduct) and PAD (plantar interossei ADduct), then logic can tell you where these muscles insert (Latin, inter = between + os = bone) | 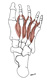 |
| plantar interosseous, in foot (N531, N535, N536, N537,TG3-46,TG3-51,TG3-52) |
base and medial side of metatarsals 3-5 | bases of proximal phalanges and extensor expansions of digits 3-5 | adduct digits 3-5 (move these digits toward the midline of the foot as defined by the second digit),flex metatarsophalangeal and extend interphalangeal joints of digits 3-5 | deep branch of lateral plantar nerve | plantar arterial arch; plantar metatarsal aa. | remember PAD (plantar interossei ADduct) and DAB (dorsal interossei ABduct), and logic will tell you where these muscles must insert (Latin, inter = between + os = bone) |  |
Nerves |
|||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nerve | Source | Branches | Motor | Sensory | Notes |
| fibular, common (N541,TG3-39) |
sciatic | lateral sural cutaneous, superficial and deep fibular nn. | superficial fibular br.: muscles of lateral compartment of leg (fibularis longus and brevis mm.); deep fibular br.: mm. of anterior compartment of leg (tibialis anterior, extensor hallucis longus, extensor digitorum longus, fibularis tertius); mm. of dorsum of foot (extensor digitorum brevis and extensor hallucis brevis) | superficial fibular: distal 1/3 of anterior leg; dorsum of foot excluding web between great toe and 2nd toe and distal interphalangeal segments of all toes; deep fibular: skin of the web between great and 2nd toes | peroneal is old terminology which has been replaced by fibular |
| fibular, superficial (N542,TG3-65) |
common fibular | medial dorsal cutaneous n. to medial side of foot; dorsal digital nn. to lateral 3 digits | muscles of lateral compartment of leg (fibularis longus and brevis mm.) | distal 1/3 of anterior leg; dorsum of foot excluding web between great toe and 2nd toe and distal interphalangeal segments of all toes; | |
| fibular, deep (N542,TG3-65) |
common fibular | one proper digital br. to the 1st and 2nd toes | mm. of anterior compartment of leg (tibialis anterior, extensor hallucis longus, extensor digitorum longus, fibularis tertius); mm. of dorsum of foot (extensor digitorum brevis and extensor hallucis brevis) | skin of the web between great and 2nd toes | peroneal is old terminology which has been replaced by fibular |
| peroneal, nn. | SEE: fibular | peroneal is old terminology which has been replaced by fibular | |||
| plantar, medial (N541,TG3-39) |
tibial | plantar cutaneous brs., proper plantar digital (medial side of hallux), common plantar digital (1st-3rd) | abductor hallucis, flexor hallucis brevis, flexor digitorum brevis, 1st lumbrical | skin of medial plantar surface of foot & plantar surface of medial 3 1/2 toes (and nail bed of these digits) | |
| plantar, lateral (N541,TG3-39) |
tibial | superficial & deep brs. | quadratus plantae, abductor digiti minimi, flexor digiti minimi brevis, lateral 3 lumbricals, adductor hallucis, plantar & dorsal interossei | skin of lateral plantar surface of foot & plantar surface of lateral 1 1/2 digits (and nail bed of these digits) | |
| plantar digital, common (N541,TG3-39) |
medial plantar (1st-3rd); superficial br. of lateral plantar (4th) | proper plantar digital nn. | 1st lumbrical | skin of plantar surface of toes (except medial side of hallux & lateral side of 5th toe) & nail bed of these toes | |
| plantar digital, proper (N541,TG3-39) |
common plantar digital, medial plantar (to medial side of great toe), superficial br. of lateral plantar (to lateral side of 5th toe) | flexor hallucis brevis (from plantar digital on medial side of great toe) | skin of plantar surface of toes & dorsal surface of distal interphalangeal segment (including nail bed) | ||
Arteries |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Artery | Source | Branches | Supply | Notes |
| plantar, medial (N535,TG3-51) |
posterior tibial | digital brs. (3) | superficial foot medially | anastomoses with plantar metatarsal aa., but does not usually participate in formation of the plantar arch |
| plantar, lateral (N535,TG3-51) |
posterior tibial | becomes continuous with the plantar arch; proper plantar digital a. to lateral side of 5th digit | deep foot; the plantar arterial arch and its brs. supply the toes, including the distal phalangeal segment dorsally | |
| arch, plantar arterial (N536,TG3-53) |
lateral plantar | plantar metatarsal aa. (4) | deep foot; its plantar metatarsal brs. and their brs. supply the toes, including the distal phalangeal segment dorsally | anastomoses with the deep plantar br. of the dorsalis pedis a. |
| tibial, anterior (N520,TG3-38) |
popliteal | anterior & posterior tibial recurrent; anterior, medial & lateral malleolar; dorsalis pedis | anterior leg, dorsal & deep foot | anterior tibial a. becomes continuous with the dorsalis pedis a.; name change occurs at the level of the ankle joint |
| dorsalis pedis (N520,TG3-38) |
anterior tibial a. | lateral & medial tarsal aa., arcuate a., 1st dorsal metatarsal a., deep plantar a. | dorsal aspect of foot; anastomoses with plantar arterial arch | the anterior tibial artery continues as the dorsalis pedis; the name change occurs at the level of the ankle (Latin, pes = foot) |
| plantar, deep (N520,TG3-38) |
dorsalis pedis | deep foot | anastomoses with lateral plantar a. to form the plantar arterial arch | |
Topographic Anatomy |
||
|---|---|---|
| Structure/Space | Boundaries/Description | Significance |
| anterior compartment (extensor), leg (N519,TG3-37) |
tibia, fibula, interosseous membrane, anterior intermuscular septum | contains tibialis anterior, extensor hallucis longus, extensor digitorum longus, fibularis tertius; also anterior tibial artery, deep fibular nerve |
| extensor retinaculum, superior (N530,TG3-45) |
strong band of deep fascia passing from the fibula to the tibia, proximal to the malleoli | binds down the tendons of the muscles in the anterior compartment, preventing bowstringing during dorsiflexion of the ankle (Latin, retinaculum = a band or halter) |
| extensor retinaculum, inferior (N530,TG3-45) |
a Y-shaped band of fascia attached laterally to the anterosuperior surface of the calcaneus | forms a strong loop around the tendons of the fibularis tertius and extensor digitorum longus muscles (Latin, retinaculum = a band or halter) |
| fibular retinaculum, superior (N529,TG3-60) |
a band of deep fascia that extends from the tip of the lateral malleolus to the calcaneus | binds down the tendons of the fibularis longus and brevis (Latin, retinaculum = a band or halter) |
| lateral compartment (evertor), leg (N519, N521,TG3-36,TG3-37) |
anterior & posterior intermuscular septa, fibula | contains: fibularis longus & brevis mm.; superficial fibular nerve |
| calcaneometatarsal ligament (N532,TG3-48) |
deep fascia forming an investment of the plantar surface of the lateral compartment of the foot | continuous with the plantar aponeurosis |
| plantar aponeurosis (N532,TG3-48) |
deep fascia forming an investment of the plantar surface of the central and medial compartments of the foot | continuous with the calcaneometatarsal ligament |
| medial compartment, foot (N533,TG3-49) |
compartment of the great toe | contains: abductor hallucis and flexor hallucis brevis mm., tendon of flexor hallucis longus m., medial plantar a., v., & n. |
| lateral compartment, foot | compartment of the little (5th) toe | contains: abductor digiti minimi and flexor digiti minimi brevis mm., branches of lateral plantar a., v., & n. |
| central compartment, foot (N533,TG3-49) |
associated with the lateral 4 toes | contains: flexor digitorum brevis & quadratus plantae mm. & lumbrical mm., tendons of flexor digitorum longus m., branches of lateral plantar a., v., & n. |
| adductor-interosseous compartment, foot | deepest of the foot compartments | contains: adductor hallucis & plantar & dorsal interossei mm., deep branch of lateral plantar n. & plantar arterial arch |
| medial longitudinal arch, foot | formed by talus, navicular, cuneiforms, medial 3 metatarsals | supported by spring ligament (plantar calcaneonavicular), assisted by tibialis anterior m. |
| lateral longitudinal arch, foot | formed by calcaneus, cuboid, lat. 2 metatarsals | supported by long & short plantar ligaments, assisted by fibularis longus m. |
| transverse arch, foot | formed by cuneiforms & cuboid | supported by long & short plantar ligaments, assisted by fibularis longus & tibialis anterior & posterior mm. |
| tarsal sinus | space between the neck of the talus and the calcaneus | contains the interosseous talocalcaneal ligament |
| The material presented in these tables is contained in the book: MedCharts Anatomy by Thomas R. Gest & Jaye Schlesinger Published by ILOC, Inc., New York Copyright © 1995, unauthorized use prohibited. |
The excellent editorial assistance of Dr. Pat Tank, UAMS is gratefully acknowledged. |