

|
|
||||||||||||
Anatomy Tables - Hip & Posterior Thigh & Leg |
|||||||||||||
Osteology |
|||
|---|---|---|---|
| Bone | Structure | Description | Notes |
| ischium (N486,TG6-04) |
the "V"-shaped bone that forms the posteroinferior part of the pelvis | one of the three bones that form the os coxae: ilium, ischium, pubis | |
| ischial spine (N486,TG6-04) |
the spine that arises just superior to the lesser sciatic notch | it is the site of attachment of the sacrospinous ligament and the site of origin of the superior gemellus m. (Greek, ischion = hip joint) | |
| ischial tuberosity (N486,TG6-04) |
the roughened projection that protrudes posteroinferiorly from the body of the ischium | it is the site of attachment of the sacrotuberous ligament; it is the site of origin of the inferior gemellus m., quadratus femoris m. and the hamstring mm. (semitendinosus, semimembranosus, long head of biceps femoris, ischiocondylar portion of the adductor magnus) (Greek, ischion = hip joint) | |
| lesser sciatic notch (N486,TG6-04) |
the notch located between the ischial tuberosity and the ischial spine | the lesser sciatic notch is converted to the lesser sciatic foramen by the sacrospinous and sacrotuberous ligaments | |
| femur (N489,TG3-06, TG3-07) |
the bone of the thigh | the femur is the longest and strongest bone in the body | |
| head | smooth, rounded proximal end | the head of the femur articulates with the acetabulum of the pelvis | |
| neck | the constricted area distal to the head of the femur | most of the blood supply to the head of the femur courses along the surface of the neck; fractures of the neck of the femur may result in avascular necrosis of the head | |
| greater trochanter | a large process that projects superiorly from the junction of the neck and shaft of the femur | the greater trochanter is the insertion site of the gluteus medius m., gluteus minimus m., piriformis m. and obturator internus m. (Greek, trochanter = a runner or roller, from trochos, a wheel. Originally used for the head of the femur, which turns like a wheel in its socket. Eventually it came to mean the bony processes of the femur) | |
| lesser trochanter | a large process that projects from the posteromedial surface of the femur just distal to neck | it is the insertion site of the common tendon of the psoas major and iliacus mm. (iliopsoas m.) (Greek, trochanter = a runner or roller, from trochos, a wheel. Originally used for the head of the femur, which turns like a wheel in its socket. Eventually it came to mean the bony processes of the femur) | |
| trochanteric fossa | a depression on the medial side of the greater trochanter on its posterior surface where the greater trochanter joins the neck | it is the insertion site of the obturator externus m. | |
| intertrochanteric crest | a heavy ridge on the posterior surface of the femur that connects the greater and lesser trochanters | the quadratus femoris m. inserts on the intertrochanteric crest | |
| gluteal tuberosity | a roughened area located on the posterior surface of the femur at the superior end of the lateral lip of the linea aspera | it is one of the insertion sites of the gluteus maximus m. | |
| fibula (N513,TG3-08, TG3-09) |
the slender bone on the lateral side of the leg | the fibula is not a weight-bearing bone, it is a muscle attachment bone | |
| head | the enlarged proximal end of the fibula | it articulates with the lateral condyle of tibia; the fibular collateral ligament of the knee attaches to the head of the fibula | |
| neck | the constricted portion of the fibula located just inferior to the head | fractures of the neck of the fibula can injure the common fibular n. | |
| ilium (N486,TG6-04) |
fan-shaped bone that forms the lateral prominence of the pelvis | one of three bones that form the os coxae: ilium, ischium, pubis | |
| greater sciatic notch (N486,TG6-04) |
the notch on the inferior portion of ilium located posteromedial to the ischial spine | the greater sciatic notch is converted to the greater sciatic foramen by the sacrospinous ligament and the sacrotuberous ligament | |
| os coxae (N486,TG3-04A,TG3-04B,TG3-05A,TG3-05B) |
the two coxal bones and sacrum form the pelvis | paired; the os coxae forms the lateral part of the pelvis; it is formed by three fused bones: ischium, ilium & pubis; also known as the innominate bone | |
| obturator foramen | a large foramen formed by the pubic and ischial rami | obturator means to occlude or stop up, a reference to the fact that the obturator membrane closes the obturator foramen almost completely; a site of attachment for the obturator externus m. and obturator internus m. | |
| obturator groove | groove on the inferior surface of the superior pubic ramus | marks the area of passage of the obturator vessels and n. in the obturator canal | |
| tibia (N513,TG3-09) |
the bone on the medial side of the leg | the tibia is the weight-bearing bone of the leg (Latin, tibia = a pipe or flute, or the large shin bone. Primitive musical instruments were made from reeds, horns, and other things, including the shin bones of birds and other animals) | |
| soleal line (N513,TG3-09) |
a ridge of bone that descends obliquely from lateral to medial on the posterior surface of the tibia | it is the site of origin of the soleus m. | |
| tarsal bones (N523,N524, TG3-40A, TG3-40B, TG3-41A, TG3-41B) |
the bones of the ankle | there are seven tarsal bones: talus, calcaneus, navicular, medial cuneiform, intermediate cuneiform, lateral cuneiform, cuboid | |
| talus (N523,TG3-40A,TG3-40B,TG3-41A,TG3-41B) |
the most proximal of the tarsal bones | the talus articulates with the medial malleolus of the tibia and the lateral malleolus of the fibula to form the ankle mortise joint (Latin, talus = ankle bone) | |
| body | the proximal part of the talus | its superior (trochlear) part participates in the ankle joint and its inferior part articulates with the calcaneus | |
| trochlea | the superior portion of the body of the talus that lies between the two malleoli | it has a smooth articular surface; it participates in the formation of the ankle joint (Latin, trochlea = pulley) | |
| head | the portion of the talus that projects anteriorly | it articulates with the navicular bone | |
| neck | the constricted part of the talus located proximal to the head | ||
| calcaneus (N525,TG3-40A,TG3-40B,TG3-41A,TG3-41B) |
the tarsal bone which forms the heel | it is the largest and strongest bone in the foot; a fracture of the calcaneus which separates the tuberosity from the body can be a debilitating injury (Latin, calcis = heel) | |
| calcaneal tuberosity | the inferior roughened area of the calcaneus which contacts the ground during weight-bearing | it is the attachment site of the plantar aponeurosis, abductor digiti minimi, flexor digitorum brevis, and the long plantar ligament | |
| sustentaculum tali | the shelf-like medial projection of bone located inferior to the medial malleolus | it is a shelf of bone that articulates with and supports the talus; it is grooved inferiorly by the tendon of the flexor hallucis longus m. (Latin, sustento = to hold upright) | |
| navicular (N523,TG3-40A,TG3-40B,TG3-41A,TG3-41B) |
the tarsal bone located distal to the talus and proximal to the three cuneiform bones | it articulates with the head of the talus and all three cuneiform bones; it is the attachment site for an important ligament (plantar calcaneonavicular or "spring" ligament) that supports the medial longitudinal arch of the foot (Latin, navicular = small boat shaped structure) | |
| cuneiform, medial (N523, TG3-40A,TG3-40B,TG3-41A,TG3-41B) |
the most medial bone in the distal row of tarsal bones | the cuneiform bones articulate with the navicular bone proximally and the bases of the metatarsal bones distally | |
| cuneiform, middle (N523, TG3-40A,TG3-40B,TG3-41A,TG3-41B) |
the intermediate bone of the three cuneiform bones | the cuneiform bones articulate with the navicular bone proximally and the bases of the metatarsal bones distally | |
| cuneiform, lateral (N523, TG3-40A,TG3-40B,TG3-41A,TG3-41B) |
the bone that is located between the middle cuneiform and the cuboid bone | the cuneiform bones articulate with the navicular bone proximally and the bases of the metatarsal bones distally | |
| cuboid (N523,TG3-40A,TG3-40B,TG3-41A,TG3-41B) |
the most lateral bone in the distal row of tarsal bones | the cuboid bone articulates with the calcaneus proximally and the fourth and fifth metatarsal bones distally | |
| metatarsals (N524,TG3-40A,TG3-40B,TG3-41A,TG3-41B) |
the bones located between the tarsal bones and the phalanges | there are five metatarsal bones in the foot | |
| base | the proximal end of the metatarsal | it articulates with the distal row of tarsal bones | |
| body | the slender shaft of the metatarsal | it is also known as the diaphysis | |
| head | the rounded distal end of the metatarsal | it articulates with the proximal phalanx of the corresponding digit | |
| phalanx (phalanges) (N524,TG3-40A,TG3-40B,TG3-41A,TG3-41B) |
the distal two or three bones in the digits of the foot | there are a total of 14 phalanges in the foot; the great toe has two phalanges (proximal and distal) and each of the other four toes has three phalanges (proximal, middle and distal); (Latin, phalanx = line of soldiers) | |
| base | the proximal end of the phalanx | the base of the proximal phalanx articulates with the head of the corresponding metatarsal bone; the base of the middle or distal phalanx articulates with the head of the next most proximal phalanx | |
| body | the slender shaft of the phalanx | also known as the diaphysis; the body of the distal phalanx is very short | |
| head | the distal end of the phalanx | the proximal, middle and distal phalanges each have a head; the head of a proximal or middle phalanx articulates with the base of the next most distal phalanx | |
Ligaments |
||
|---|---|---|
| Ligaments | Description | Significance |
| sacrospinous ligament (N503,N353,TG3-07,TG6-06) |
the ligament that connects the ischial spine to the lateral surface of the sacrum and coccyx | together with the sacrotuberous ligament, it converts the greater and lesser sciatic notches into greater and lesser sciatic foramina |
| sacrotuberous ligament (N503,N353,TG3-07,TG6-06) |
the ligament that connects the ischial tuberosity to the lateral surface of the sacrum and coccyx | together with sacrospinous ligament, it converts the greater and lesser sciatic notches into greater and lesser sciatic foramina |
Muscles |
|||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Muscle | Origin | Insertion | Action | Innervation | Blood Supply | Notes | Image |
| gluteus maximus (N503,TG3-26) |
posterior gluteal line, posterior sacrum and coccyx, sacrotuberous ligament | upper fibers: iliotibial tract; lowermost fibers: gluteal tuberosity of femur | extends thigh and trunk, laterally rotates femur | inferior gluteal nerve | inferior gluteal a. and superficial br. of superior gluteal a. | (Greek, gloutos = buttock) | 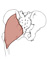 |
| gluteus medius (N503,TG3-26) |
ilium between posterior and anterior gluteal lines | greater trochanter of femur | abducts and medially rotates thigh | superior gluteal nerve | deep br. of superior gluteal a. | (Greek, gloutos = buttock) | 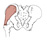 |
| gluteus minimus (N503,TG3-26) |
ilium between anterior and inferior gluteal lines | greater trochanter of femur | abducts and medially rotates thigh | superior gluteal nerve | deep br. of superior gluteal a. | (Greek, gloutos = buttock) | 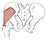 |
| tensor fasciae latae (N494,N503,TG3-17) |
anterior part of iliac crest, anterior superior iliac spine | iliotibial tract | flexes, abducts, and medially rotates the thigh | superior gluteal nerve | deep br. of superior gluteal a. | 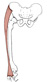 |
|
| piriformis (N503,TG3-26) |
anterior surface of sacrum | upper border of greater trochanter of femur | laterally rotates and abducts thigh | ventral rami of S1-S2 | lateral sacral, superior and inferior gluteal aa. | piriformis leaves the pelvis by passing through the greater sciatic foramen (Latin, piriformis = pear shaped) | 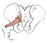 |
| obturator internus (N495,N503,TG3-26,TG3-28) |
margin of obturator foramen and internal surface of obturator membrane | greater trochanter, medial surface above the trochanteric fossa | laterally rotates and abducts thigh | nerve to obturator internus (L5,S1-2) | obturator, inferior gluteal a. | obturator internus leaves the pelvis by passing through the lesser sciatic foramen | 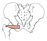 |
| superior gemellus (N503,TG3-26,TG3-28) |
ischial spine | obturator internus tendon | laterally rotates the femur | nerve to the obturator internus m. | inferior gluteal a. | gemellus is a Latin word that means "little twin" | 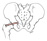 |
| inferior gemellus (N503,TG3-26,TG3-28) |
ischial tuberosity | obturator internus tendon | laterally rotates the femur | nerve to quadratus femoris | inferior gluteal a. | (Latin, gemellus = little twin) | 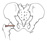 |
| quadratus femoris (N503,TG3-26,TG3-28) |
lateral border of ischial tuberosity | quadrate line below intertrochanter crest | laterally rotates thigh | nerve to quadratus femoris | inferior gluteal a. | nerve to quadratus femoris also innervates inferior gemellus m. (Latin, quadratus = square) | 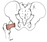 |
| biceps femoris (N495,TG3-29) |
long head: ischial tuberosity; short head: lateral lip of linea aspera | head of fibula and lateral condyle of the tibia | extends thigh, flexes leg | long head: tibial nerve; short head: common fibular (peroneal) nerve | perforating brs. of deep femoral a. | 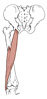 |
|
| semitendinosus (N495,TG3-29) |
lower, medial surface of ischial tuberosity (common tendon with biceps femoris m.) | medial surface of tibia (via pes anserinus) | extends thigh, flexes leg | tibial nerve | perforating brs. of deep femoral a. | pes anserinus is the common insertion for the gracilis, sartorius, and semitendinosus mm. | 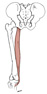 |
| semimembranosus (N495,TG3-29) |
upper, outer surface of ischial tuberosity | medial condyle of tibia | extends thigh, flexes leg | tibial nerve | perforating brs. of deep femoral a. | 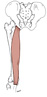 |
|
| gastrocnemius (N516,N517,TG3-33) |
femur; medial head: above medial femoral condyle; lateral head: above lateral femoral condyle | dorsum of calcaneus via calcaneal (Achilles') tendon | flexes leg, plantarflexes foot | tibial nerve | genicular and sural brs. of popliteal a. | the calcaneal tendon of gastrocnemius & soleus is the thickest & strongest tendon in the body (Greek, gaster = belly + kneme = leg, the belly of the leg) |  |
| plantaris (N517,TG3-34) |
above lateral femoral condyle (above lateral head of gastrocnemius) | dorsum of calcaneus medial to calcaneal tendon | flexes leg, plantarflexes foot | tibial nerve | genicular and sural brs. of popliteal a. |  |
|
| soleus (N517,TG3-34) |
posterior surface of head & upper shaft of fibula, soleal line of tibia | dorsum of calcaneus via the calcaneal (Achilles') tendon | plantarflexes foot | tibial nerve | inferior medial genicular and sural brs. of popliteal a. | soleus and the 2 heads of gastrocnemius are sometimes called the triceps surae muscle (Latin, soleus = sole of the foot) | 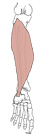 |
| popliteus (N518,TG3-31) |
lateral condyle of femur (via a round tendon) | posterior surface of tibia above soleal line | flexes and rotates leg medially (with foot planted, rotates thigh laterally) | tibial nerve | genicular brs. of popliteal a. | popliteus unlocks the knee joint to initiate flexion of the leg (Latin, poples = the back of the knee) | 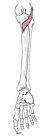 |
| flexor hallucis longus (N518,TG3-35) |
lower two/thirds of posterior surface of fibula | base of distal phalanx of hallux | flexes metatarsophalangeal and proximal interphalangeal joints of hallux; plantarflexes foot | tibial nerve | fibular a. | flexor hallucis longus is very important in the "push off" part of the normal gait (Latin, hallex = great toe) | 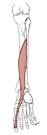 |
| flexor digitorum longus (N518,TG3-35) |
middle half of posterior surface of tibia | bases of distal phalanges of digits 2-5 | flexes metatarsophalangeal, proximal interphalangeal and distal interphalangeal joints of digits 2-5; plantarflexes foot | tibial nerve | posterior tibial a. | flexor digitorum longus in the leg is equivalent to the flexor digitorum profundus m. of the arm | 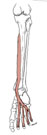 |
| tibialis posterior (N518,TG3-35) |
interosseous membrane, posteromedial surface of fibula, posterolateral surface of tibia | tuberosity of navicular & medial cuneiform, metatarsals 2-4 | plantarflexes foot and inverts foot | tibial nerve | posterior tibial a. | acts as both an antagonist (dorsiflexion/plantar flexion) and a synergist (inversion) of tibialis anterior | 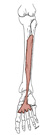 |
Nerves |
|||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nerve | Source | Branches | Motor | Sensory | Notes |
| sacral plexus (N499,TG3-25A,TG3-25B) |
lumbosacral trunk (ventral primary rami of L4-L5), ventral primary rami of S1-S4 | superior & inferior gluteal nn., n. to obturator internus, n. to quadratus femoris, sciatic n., n. to piriformis, posterior femoral cutaneous n., pudendal n., n. to pelvic diaphragm, pelvic splanchnic nn. | mm. of pelvic diaphragm and perineum, posterior hip, posterior thigh, leg & foot | skin of perineum, posterior thigh, leg & foot (excluding medial side of leg & foot) | (Latin, plexus = a braid, a network of nerves, blood vessels or lymphatic vessels) |
| femoral cutaneous, posterior (N540, TG3-28) |
sacral plexus (ventral primary rami of S1-S3) | inferior cluneal nn.; perineal br. | skin of lower buttock & posterior thigh | (Latin, cutis = skin) | |
| medial sural cutaneous (N540, TG3-39) |
tibial n. | no named branches | none | skin of the posterior surface of the leg; skin of the lateral side of the foot | unites with fibular communicating br. to form the sural n. (Latin, cutis = skin) |
| lateral sural cutaneous (N540, TG3-39) |
common fibular n. | fibular communicating br. | none | skin of the lateral side of the leg | contains postganglionic sympathetic axons for supply of sweat glands, arrector pili mm. and blood vessels, as do ALL cutaneous sensory nerves (Latin, cutis = skin) |
| sural n. (N540, TG3-39, Practical) |
formed by the union of the fibular communicating br. of the lateral sural cutaneous n. and the medial sural cutaneous nn. | lateral calcaneal brs., lateral dorsal cutaneous n. of the foot | none | skin of the posterior surface of the lower leg; skin of the lateral side of the foot | sural n. courses posterior to the lateral malleolus at the ankle with the lesser saphenous v.(Latin, sura= the calf of the leg) |
| gluteal, inferior (N499,TG3-26) |
sacral plexus (ventral primary rami of L5, S1-S2) | gluteus maximus | passes through greater sciatic foramen inferior to piriformis m. | ||
| gluteal, superior (N485,N499N503,TG3-26) |
sacral plexus (ventral primary rami of L4-L5, S1) | superior & inferior brs. | gluteus medius & minimus, tensor fasciae latae | passes through greater sciatic foramen superior to piriformis m. | |
| sciatic (502,TG3-26) |
sacral plexus (ventral primary rami of L4-L5, S1-S3) | tibial, common fibular (peroneal) | (via its tibial & common fibular branches) semitendinosus, semimembranosus, biceps femoris, ischioconylar part of adductor magnus, muscles of leg & foot | skin of leg & foot (excluding medial side of leg & foot) | sciatic has no direct muscular brs., only 2 terminal brs. - tibial & common fibular nn. |
| fibular, common (N540,TG3-65A,TG3-65B) |
sciatic | lateral sural cutaneous, superficial and deep fibular nn. | short head of biceps femoris; superficial fibular br.: muscles of lateral compartment of leg (fibularis longus and brevis mm.); deep fibular br.: mm. of anterior compartment of leg (tibialis anterior, extensor hallucis longus, extensor digitorum longus, fibularis tertius); mm. of dorsum of foot (extensor digitorum brevis and extensor hallucis brevis) | superficial fibular: distal 1/3 of anterior leg; dorsum of foot excluding web between great toe and 2nd toe and distal interphalangeal segments of all toes; deep fibular: skin of the web between great and 2nd toes | peroneal is old terminology which has been replaced by fibular |
| tibial (N540,TG3-66) |
sciatic | medial sural cutaneous, medial calcaneal brs., medial & lateral plantar nn. | semimembranosus, semitendinosus, long head of biceps femoris, ischiocondylar portion of adductor magnus; mm. of superficial and deep posterior compartments of leg (gastrocnemius, soleus, plantaris, tibialis posterior, flexor hallucis longus, flexor digitorum longus); muscles of plantar side of the foot | ||
| pudendal (N499,N502, N503, TG3-26) |
sacral plexus (ventral primary rami of S2-S4) | inferior rectal n., perineal n., dorsal n. of clitoris/penis | its branches supply: external anal sphincter, bulbospongiosus, ischiocavernosus, superficial & deep transverse perineus, sphincter urethrae, sphincter urethrovaginalis, compressor urethrae | its branches supply: skin of anus, posterior scrotum/labum majus, clitoris/penis | passes through pudendal canal formed by fascia on the medial surface of the obturator internus m. ( Latin, pudendus = ashamed, the term referred to "the shameful parts".) |
| to obturator internus (N499,N503, TG3-26) |
sacral plexus (ventral primary rami of L5, S1-S2) | obturator internus, superior gemellus | |||
| to quadratus femoris (N499,TG3-25A, TG3-25B) |
sacral plexus (ventral primary rami of L4-L5, S1) | quadratus femoris, inferior gemellus | |||
Arteries |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Artery | Source | Branches | Supply | Notes |
| gluteal, inferior (N499,TG3-26) |
internal iliac, anterior division | gluteus maximus, hip joint | participates in the formation of the cruciate anastomoses of the hip (Greek, gloutos = buttock) | |
| gluteal, superior (N485,N499, N503,TG3-26) |
internal iliac, posterior division | superficial br., deep br. | gluteus maximus, medius & minimus, hip joint | |
| internal pudendal (N499, TG3-26) |
internal iliac a., anterior division | inferior rectal a., perineal a., artery of the bulb of the clitoris/penis, urethral a., deep clitoral/penile a., dorsal clitoral/penile a. | anus, muscles of the superficial and deep perineal spaces, clitoris/penis, posterior aspect of the scrotum/labium majus | internal pudendal a. is the primary blood supply to the perineum ( Latin, pudendus = ashamed, the term referred to "the shameful parts".) |
| femoral, deep | femoral | medial & lateral circumflex femoral aa., perforating aa. (~3 or 4) | hip joint, proximal thigh, posterior thigh | the primary blood supply to muscles of the posterior compartment of the thigh |
| popliteal (N517,TG3-31) |
femoral a. | anterior tibial a., posterior tibial a., 5 genicular brs. | knee, leg and foot | the popliteal a. is the continuation of the femoral a.; the name change occurs at the adductor hiatus (Latin, poples = the back of the knee) |
| genicular, middle (N512) |
popliteal | cruciate ligaments & deep structures of knee | anastomoses with other genicular brs. of popliteal a., circumflex fibular a. & anterior tibial recurrent a. to form genicular anastomosis (Latin, genicular = to bend around the knee) | |
| genicular, superior lateral (N517,TG3-38AB) |
popliteal | lateral aspect of knee | anastomoses with other genicular brs. of popliteal a., circumflex fibular a. & anterior tibial recurrent a. to form genicular anastomosis (Latin, genicular = to bend around the knee) | |
| genicular, superior medial (N517,TG3-38AB) |
popliteal | medial aspect of knee | anastomoses with other genicular brs. of popliteal a., circumflex fibular a. & anterior tibial recurrent a. to form genicular anastomosis (Latin, genicular = to bend around the knee) | |
| tibial, posterior (N518,TG3-38AB) |
popliteal | fibular (peroneal), circumflex fibular, nutrient a. of tibia, communicating br., posterior medial malleolar brs., medial calcaneal brs., lateral & medial plantar aa. | posterior & lateral leg, plantar aspect of foot | posterior tibial bifurcates on the medial side of the foot to give rise to the medial and lateral plantar aa. |
| fibular (N518,TG3-38AB) |
posterior tibial | nutrient br., lateral malleolar br., communicating br., perforating br. | lateral leg & ankle | anastomoses at ankle with anterior & posterior tibial aa. |
| tibial, anterior (N520,TG3-38AB) |
popliteal | anterior & posterior tibial recurrent; anterior, medial & lateral malleolar; dorsalis pedis | anterior leg, dorsal & deep foot | anterior tibial a. becomes continuous with the dorsalis pedis a.; name change occurs at the level of the ankle joint |
Veins |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vein | Tributaries | Drains Into | Region Drained | Notes |
| saphenous, lesser (N545, TG3-03) |
lateral end of dorsal venous arch of foot | popliteal v. | superficial lateral foot & leg | (Saphenous, arabic for "al safin" = hidden, for this vein does not show through the skin) |
| popliteal (N517,TG3-31) |
anterior & posterior tibial vv., lesser saphenous v. | continues as femoral v. | foot & leg | lies posterior to popliteal a. within popliteal fossa |
Topographic Anatomy |
||
|---|---|---|
| Structure/Space | Boundaries/Description | Significance |
| greater sciatic foramen | the passageway for structures entering or leaving the pelvis | the piriformis m. occupies this space along with all lower limb vessels and nerves entering the gluteal region |
| lateral compartment (gluteal), thigh | located posterolateral to hip joint | contains: tensor fasciae latae m., gluteus maximus, medius & minimis mm., piriformis m., superior & inferior gemellus mm., quadratus femoris m.; obturator internus tendon |
| lesser sciatic foramen | the passageway for structures entering or leaving the perineum | |
| posterior compartment (hamstring), thigh | located posterior to femur | contains: semimembranosus, semitendinosus, biceps femoris mm.; sciatic nerve |
| popliteal fossa (N495,TG3-31) |
superomedial - tendons of semimembranosus & semitendinosus, superolateral - tendon of biceps femoris, inferior - medial & lateral heads of gastrocnemius | contains: popliteal a. & v. and their branches; tibial and common fibular nn.; popliteus m. (Latin, poples = the back of the knee) |
| sacroiliac joint (N341,N354,TG6-06A, TG6-06B) |
the articulation between the ala of the sacrum and the auricular surface of the ilium | a synovial joint; the fibrous articular capsule is thickened dorsally and ventrally to form the sacroiliac ligaments; because of the interlocking nature of the joint surfaces and the strong sacroiliac ligaments, only limited movement is permitted at the sacroiliac joint |
| posterior compartment (flexor), leg | tibia, fibula, interosseous membrane, posterior intermuscular septum | contains: superficially - gastrocnemius, soleus, plantaris mm.; deeply - popliteus, tibialis posterior, flexor digitorum longus, flexor hallucis longus mm.; also contains posterior tibial vessels & tibial n. |
| fascia, crural (N544,TG3-03) |
deep fascia forming tubular investment of leg | continuous with fascia lata at knee; connected to fibula by anterior & posterior intermuscular septa; thickened near ankle as extensor & flexor retinacula (Latin, crural = the legs) |
| flexor retinaculum (N511,TG3-35) |
a band of deep fascia that extends from the tip of the medial malleolus to the calcaneus | binds, in order anteromedial to posterolateral, tendon of tibialis posterior, flexor digitorum longus, posterior tibial artery and vein, tibial nerve, and tendon of flexor hallucis longus(Latin, retinaculum = a band or halter) |
| The material presented in these tables is contained in the book: MedCharts Anatomy by Thomas R. Gest & Jaye Schlesinger Published by ILOC, Inc., New York Copyright © 1995, unauthorized use prohibited. |
The excellent editorial assistance of Dr. Pat Tank, UAMS is gratefully acknowledged. |