

|
|
||||||||||||
Anatomy Tables - Anterior & Medial Thigh |
|||||||||||||
Osteology |
|||
|---|---|---|---|
| Bone | Structure | Description | Notes |
| femur (N489, TG3-06,TG3-07, Practical) |
the bone of the thigh | the femur is the longest and strongest bone in the body (Latin, femur = thigh) | |
| adductor tubercle | a process that projects superior to the medial epicondyle of the femur | it is the insertion site of the ischiocondylar part of the adductor magnus m. | |
| lateral epicondyle | the enlargement of bone on the lateral side of the femur just superior to the lateral condyle | it is the attachment site of the fibular collateral ligament and the site of origin of the popliteus m. (Greek, kondylos = the knob formed by the knuckle of any joint) | |
| lesser trochanter | a large process that projects from the posteromedial surface of the femur just distal to neck | it is the insertion site of the common tendon of the psoas major and iliacus mm. (iliopsoas m.) (Greek, trochanter = a runner or roller, from trochos, a wheel. Originally used for the head of the femur, which turns like a wheel in its socket. Eventually it came to mean the bony processes of the femur) | |
| linea aspera (Practical) | a vertical ridge on posterior surface of the femur | it is the insertion site of the medial (adductor) group of thigh muscles and the origin of the vastus intermedius m. and the short head of the biceps femoris m. (Latin, linea aspera = rough line, the linea aspera is a roughed longitudinal line on the posterior surface of the shaft of the femur which gives attachment to several muscles) | |
| medial epicondyle | the enlargement of bone on the medial side of the femur just superior to the medial condyle | it is the attachment site of the tibial collateral ligament of the knee joint (Greek, kondylos = the knob formed by the knuckle of any joint) | |
| pectineal line | a prominent intermediate ridge extending from the central part of the linea aspera to the base of the lesser trochanter | ||
| ilium (N248,TG5-03, N486, TG3-04A, TG3-04B) |
fan-shaped bone that forms the lateral prominence of the pelvis | one of three bones that form the os coxae: ilium, ischium, pubis | |
| arcuate line | ridge running from anteroinferior to posterosuperior on the inner surface of the ilium | inferior boundary of the iliac fossa; marks the plane of transition from abdominal cavity to pelvic cavity; part of the iliopectineal line (Latin, arcuate = bowed) | |
| anterior inferior iliac spine | inferior to anterior superior iliac spine | attachment site of straight head of rectus femoris m. | |
| anterior superior iliac spine | spine at the anterior end of the iliac crest | lateral attachment of the inguinal ligament | |
| iliac crest | arching superior margin of the ilium that forms the rim of the "fan" | attachment for abdominal wall muscles | |
| iliac tubercle | roughened area along the outer edge of the iliac crest | ||
| posterior superior iliac spine | spine at the posterior end of the iliac crest | position marked by a dimpling of the skin | |
| ischium (N486,TG3-04A, TG3-04B) |
the "V"- shaped bone that forms the posteroinferior part of the pelvis | one of the three bones that form the os coxae: ilium, ischium, pubis | |
| ischial ramus | the limb of the ischium that passes anteriorly and superomedially toward the pubis | it articulates with the inferior ramus of the pubis to form ischiopubic ramus (Greek, ischion = hip joint; Latin, ramus = a branch) | |
| ischial tuberosity | the roughened projection that protrudes posteroinferiorly from the body of the ischium | it is the site of attachment of the sacrotuberous ligament; it is the site of origin of the inferior gemellus m., quadratus femoris m. and the hamstring mm. (semitendinosus, semimembranosus, long head of biceps femoris, ischiocondylar portion of the adductor magnus) (Greek, ischion = hip joint) | |
| patella (N507, N511,TG3-06,TG3-56) |
the bone that forms the knee cap | the patella is a sesamoid bone in the tendon of the quadriceps femoris muscle; it provides a protective function by withstanding the grinding forces of the quadriceps femoris tendon against the patellar surface of the femur, especially in full knee flexion (Latin, a kneecap) | |
| pubis (N486,TG3-04A, TG3-04B) |
an angulated bone that forms the anterior part of the pelvis | one of three bones that form the os coxae: ilium, ischium, pubis; its body forms 1/5 of the acetabulum; its symphyseal surface unites with the pubis of the opposite side to form the pubic symphysis; the superior and inferior pubic rami participate in the formation of the obturator foramen | |
| body | superolateral portion of the pubis | the body of the pubis forms about 1/5 of the acetabulum | |
| inferior ramus | inferior "limb" that passes inferolaterally from the pubic symphysis | articulates with the ischial ramus to form the ischiopubic ramus; attachment site for the root of the penis/clitoris (Latin, ramus = a branch) | |
| pecten | ridge on superior surface of the superior pubic ramus | attachment point of the pectineal ligament | |
| pubic crest | ridge on the superior border of the superior ramus | attachment of rectus abdominis & pyramidalis mm. | |
| pubic tubercle | process at the lateral end of pubic crest | attachment point of the medial end of the inguinal ligament | |
| tibia (N513,TG3-08,TG3-09) |
the bone on the medial side of the leg | the tibia is the weight-bearing bone of the leg (Latin, tibia = the large shin bone) | |
| lateral condyle | the heavy prominence on the lateral side of the proximal end of the tibia | the lateral condyle articulates with the lateral condyle of the femur and with the head of the fibula (Greek, kondylos = the knob formed by the knuckle of any joint) | |
| medial condyle | the heavy prominence on the medial side of the proximal end of the tibia | the medial condyle articulates with the medial condyle of the femur; it is larger than the lateral condyle of the tibia (Greek, kondylos = the knob formed by the knuckle of any joint) | |
| medial malleolus | the large bony prominence on the medial side of the ankle | the medial malleolus of the tibia forms the medial side of the ankle joint; it articulates with the medial surface of the talus (Latin, malleus = hammer) | |
| tibial tuberosity | the roughened protuberance on the anterior surface of the tibia located just distal to the condyles | it is the attachment site of the patellar ligament, which represents the insertion of the quadriceps femoris tendon | |
| fibula (N495, TG3-08, TG3-09) |
the slender bone on the lateral side of the leg | the fibula is not a weight-bearing bone, it is a muscle attachment bone (Latin, fibula = that which fastens) | |
| lateral malleolus | the enlarged distal end of the fibula | the lateral malleolus of the fibula forms the lateral side of the ankle joint; it articulates with the lateral surface of the talus; forcible lateral displacement of the foot can cause the fibula to fracture superior to the lateral malleolus, a condition called a Pott's fracture (Latin, malleus = hammer) | |
Joints and Ligaments |
||
|---|---|---|
| Joint | Description | Significance |
| inguinal ligament (N250, N492,TG3-16,TG5-04) |
the ligament that connects the anterior superior iliac spine with the pubic tubercle | the inguinal ligament is a specialization of the inferior border of the external abdominal oblique aponeurosis; it is the site of origin for a part of the internal abdominal oblique muscle and for a part of the transversus abdominis muscle; also known as: Poupart's ligament |
| pubic symphysis (N248,TG5-03) |
symphysis | midline joint uniting the pubic bodies (Greek, symphysis = a growing together) |
| patellar ligament (N492,TG3-16) |
stretches from the apex of the patella distally to the tibial tuberosity | continuation of quadriceps tendon |
| patellar retinacula (N492,TG3-16) |
aponeurotic insertions of the quadriceps muscle lateral and medial to the patellar ligament | reinforces the knee joint capsule anteriorly |
Muscles |
|||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Muscle | Origin | Insertion | Action | Innervation | Blood Supply | Notes | Image |
| iliopsoas (N492,TG3-16) |
combination of iliacus (from iliac fossa) & psoas major (from lumbar vertebrae) | lesser trochanter of femur | flexes thigh; flexes & laterally bends lumbar spine | ventral primary rami of L2-L4 and branches from femoral nerve | iliolumbar and deep circumflex iliac aa. | 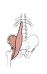 |
|
| sartorius (N492,TG3-16) |
anterior superior iliac spine | medial surface of tibia (pes anserinus) | flexes, abducts, and laterally rotates thigh; flexes leg | femoral nerve | femoral, lateral femoral circumflex, and descending genicular aa. | (Latin, sartor = tailor, because its actions put the lower limb in the traditional cross-legged seated position of a tailor) |  |
| quadriceps femoris (N492,TG3-16) |
composed of 4 muscles: rectus femoris, vastus lateralis, vastus intermedius & vastus medialis | tibial tuberosity via patellar ligament | extends knee; rectus femorus flexes thigh | femoral nerve | femoral and lateral femoral circumflex aa. | 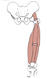 |
|
| rectus femoris (N492,TG3-16) |
straight head: anterior inferior iliac spine; reflected head: above superior rim of acetabulum | patella and tibial tuberosity (via patellar ligament) | extends leg, flexes thigh | femoral nerve | femoral and lateral femoral circumflex aa. | rectus femoris is part of the quadriceps femoris muscle | 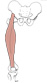 |
| vastus lateralis (N492,TG3-16) |
lateral intermuscular septum, lateral lip of linea aspera and gluteal tuberosity | patella and lateral patellar retinaculum | extends leg | femoral nerve | femoral and lateral femoral circumflex aa. | vastus lateralis is part of the quadriceps femoris muscle (Latin, vastus = huge) |  |
| vastus medialis (N492,TG3-16) |
medial intermuscular septum, medial lip of linea aspera | patella and medial patellar retinaculum | extends leg | femoral nerve | femoral and lateral femoral circumflex aa. | vastus medialis is part of the quadriceps femoris muscle (Latin, vastus = huge) |  |
| vastus intermedius (N492,TG3-16) |
anterior and lateral surface of femur | patella | extends leg | femoral nerve | femoral and lateral femoral circumflex aa. | vastus intermedius is part of the quadriceps femoris muscle (Latin, vastus = huge) | 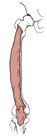 |
| pectineus (N492,TG3-16) |
pecten of pubis | pectineal line of femur | adducts, flexes, and medially rotates thigh | femoral nerve and occasionally anterior division of obturator nerve | medial femoral circumflex aa. | 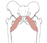 |
|
| gracilis (N492,TG3-16) |
pubic symphysis and inferior pubic ramus | medial surface of tibia (via pes anserinus) | adducts thigh, flexes leg, flexes and medially rotates thigh | anterior division of obturator nerve | obturator and deep femoral aa. | pes anserinus is the common insertion of the gracilis, sartorius, and semitendinosus mm. (Latin, gracilis = slender) | 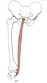 |
| adductor longus (N492,TG3-19) |
medial portion of superior pubic ramus | linea aspera of femur | adducts, flexes, and medially rotates femur | anterior division of obturator nerve | obturator and deep femoral aa. | 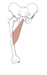 |
|
| adductor brevis (N493, N501,TG3-20, TG3-21) |
inferior pubic ramus | pectineal line and linea aspera (deep to pectineus and adductor longus mm.) | adducts, flexes, and medially rotates femur | anterior division of obturator nerve | obturator and deep femoral aa. | anterior and posterior divisions of the obturator nerve lie on the anterior and posterior surfaces of adductor brevis | 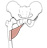 |
| adductor magnus (N493,TG3-21) |
ischiopubic ramus and ischial tuberosity | linea aspera of femur; ischiocondylar part inserts on adductor tubercle | adducts, flexes, and medially rotates femur; extends femur (ischiocondylar part) | posterior division of obturator nerve and tibial nerve (ischiocondylar part) | obturator and deep femoral aa. | the ischiocondylar part of adductor magnus is a hamstring muscle by embryonic origin and action, so it is innervated by the tibial nerve |  |
Nerves |
|||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nerve | Source | Branches | Motor | Sensory | Notes |
| femoral (N500, N544,TG3-24,TG3-63) |
lumbar plexus (ventral primary rami of L2-L4) | anterior femoral cutaneous brs., saphenous n., nn. to: sartorius, rectus femoris, vastus lateralis, vastus intermedius, vastus medialis, pectineus | sartorius, rectus femoris, vastus lateralis, vastus intermedius, vastus medialis, pectineus | skin of anterior thigh | passes under inguinal ligament lateral to femoral a. |
| femoral cutaneous, anterior (N500, N544,TG3-24,TG3-63) |
femoral | skin of anterior thigh | (Latin, cutis = skin) | ||
| saphenous (N500, N544,TG3-24,TG3-63) |
femoral | infrapatellar br. | skin of medial leg & foot | travels with great saphenous v.; does not pass through the adductor hiatus at the knee; passes anterior to the medial malleolus at the ankle (Saphenous, arabic for "al safin" = hidden, for this vein does not show through the skin) | |
| femoral cutaneous, lateral (N500, N540, TG3-17, TG3-63) |
lumbar plexus (ventral primary rami of L2-L3) | anterior & posterior brs. | skin of lateral thigh | (Latin, cutis = skin) | |
| obturator (N501, N539,TG3-24,TG3-64) |
lumbar plexus (ventral primary rami of L2-L4) | anterior & posterior brs. | adductors of thigh: longus, brevis & magnus; gracilis, obturator externus | skin of lower medial thigh | passes through obturator canal |
| superficial fibular n. (N502, N524, TG3-65) |
common fibular n. | medial dorsal cutaneous n. to the medial side of the foot; dorsal digital nn. to the lateral 3 toes | muscles of the lateral compartment of the leg (fibularis longus and brevis mm.) | distal 1/3 of the anterior surface of the leg; dorsum of the foot excluding the skin of the web between the great toe and the 2nd toe and the distal interphalangeal segments of all toes | nail beds are supplied by nerves from the plantar surface of the foot |
| deep fibular n. (N520, N542, TG3-65, Practical1, Practical2) |
common fibular n. | one proper digital br. | muscles of the anterior compartment of the leg (tibialis anterior m., extensor hallucis longus m., extensor digitorum longus m., fibularis tertius m.) and muscles of the dorsum of the foot (extensor digitorum brevis m.and extensor hallucis brevis m.) | skin of the web between the great toe and the 2nd toe | anterior compartment syndrome - trauma to the anterior side of the leg can result in pressure buildup in the anterior compartment (from swelling or bleeding) that can damage the deep fibular n., resulting in "foot drop" |
Arteries |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Artery | Source | Branches | Supply | Notes |
| femoral (N500, N512,TG3-22, TG3-62) |
external iliac | superficial epigastric a., superficial circumflex iliac a., superficial & deep external pudendal aa., deep femoral, descending genicular, popliteal | thigh, leg & foot | the femoral a. is continuous with the popliteal a.; the name change occurs at the adductor hiatus |
| femoral, deep (N501, N512,TG3-23,TG3-62) |
femoral | medial & lateral circumflex femoral aa., perforating aa. (~3 or 4) | hip joint, proximal thigh, posterior thigh | the primary blood supply to muscles of the posterior compartment of the thigh |
| iliac, external (N501, N512,TG3-23, TG3-62) |
common iliac | inferior epigastric, deep circumflex iliac, femoral | lower limb | external iliac a. is continuous with the femoral a.; the name change occurs at the inguinal ligament; the common iliac artery bifurcates anterior to the sacroiliac articulation |
| obturator (N501, N512,TG3-23, TG3-62) |
internal iliac, anterior division | pubic br., acetabular br., anterior br., posterior br. | medial thigh & hip | anterior & posterior brs. pass on anterior and posterior sides of adductor brevis m. |
| circumflex femoral, medial (N501, N504, N512,TG3-23,TG3-62) |
deep femoral (or femoral) | ascending & descending brs. | medial thigh & hip | (Latin, circum- = around + -felx = to bend) |
| circumflex femoral, lateral (N501, N504, N512,TG3-23,TG3-62) |
deep femoral (or femoral) | ascending, transverse & descending brs. | lateral thigh & hip | (Latin, circum- = around + -felx = to bend) |
| popliteal (N512,TG3-62) |
femoral | anterior & posterior tibial; 5 genicular brs. | knee, leg & foot | the popliteal a. is the continuation of the femoral a.; the name change occurs at the adductor hiatus (Latin, poples = the back of the knee) |
Veins |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vein | Tributaries | Drains Into | Regions Drained | Notes | dorsal venous arch of foot (N544, TG3-02) |
dorsal digital vv. and dorsal metatarsal vv. | great saphenous v. medially, small saphenous v. laterally | dorsum of digits & superficial structures of dorsum of foot |
| saphenous, greater (N544, N546, TG3-02, TG3-70) |
medial end of dorsal venous arch of foot, perforating communications, superficial epigastric, superficial circumflex iliac, superficial external pudendal | femoral v. | superficial structures of medial lower limb; lower abdominal wall, perineal region | frequently used as graft material in coronary bypass surgery (Saphenous, arabic for "al safin" = hidden, for this vein does not show through the skin) |
| epigastric, superficial (N500, N544, TG3-02) |
none | greater saphenous v. | superficial fascia and skin of the lower abdominal wall | superficial epigastric v. communicates with paraumbilical vv. and may enlarge in portal hypertension, producing the sign called caput medusae |
| saphenous, lesser (N545, TG3-03) |
lateral end of dorsal venous arch of foot | popliteal v. | superficial lateral foot & leg | (Saphenous, arabic for "al safin" = hidden, for this vein does not show through the skin) |
Topographic Anatomy |
||
|---|---|---|
| Structure/Space | Boundaries/Description | Significance |
| adductor canal (N492, N500, N501,TG3-17,TG3-22,TG3-23) |
anterior - sartorius, lateral - vastus medialis, posterior - adductor longus & magnus; ends distally at adductor hiatus | contains femoral a. & v., saphenous nerve & nerve to vastus medialis m. |
| adductor hiatus (N493,TG3-21) |
medial - tendon of adductor magnus to adductor tubercle, lateral - insertion of adductor magnus into linea aspera, inferior - femur | femoral vessels pass through it to reach the posterior surface of the leg, becoming popliteal vessels (Latin, hiatus = to yawn) |
| anterior compartment (extensor), thigh | located anterior to femur | contains quadriceps femoris and sartorius mm. |
| pes anserinus (N490, N493, N506, N507,TG3-12,TG3-56, TG3-57) |
adjacent insertions of sartorius, gracilis, and semitendinosus on proximal tibia medial to tibial tuberosity | (Latin, pes = foot, anserinus = of the goose) |
| femoral canal (N262,TG3-18A,TG3-18B) |
location: medial compartment of the femoral sheath, deep to inguinal ligament; opens into the abdominal cavity superiorly at femoral ring | may be the site of a femoral hernia; usually contains a deep inguinal lymph node (node of Cloquet) |
| femoral ring (N262,TG3-18A,TG3-18B) |
medial - lacunar ligament, lateral - fascia on femoral vein, anterior - inguinal ligament, posterior - iliopectineal fascia | opening from abdominal cavity into the femoral canal |
| femoral sheath (N262,TG3-18A,TG3-18B) |
lateral compartment- for the femoral a. intermediate compartment- for the femoral v. medial compartment- the femoral canal | does not enclose the femoral nerve |
| femoral triangle (N262,TG3-18A,TG3-18B) |
superior - inguinal ligament, lateral - sartorius, medial - medial edge of adductor longus m. | contains femoral a., v. & femoral nerve branches; authors disagree on the medial boundary of this triangle |
| Hunter's canal | see adductor canal | |
| medial compartment (adductor), thigh | located medial to femur | contains: pectineus m., adductor longus, brevis & magnus mm.; gracilis m., obturator externus m. |
| saphenous hiatus | opening in fascia lata located inferior to inguinal ligament, lateral to pubic tubercle | site of passage of greater saphenous vein which joins the femoral vein; closed by cribriform fascia (Saphenous, arabic for "al safin" = hidden, for this vein does not show through the skin; Latin, hiatus = to yawn) |
| subsartorial canal | see adductor canal | |
Fascia |
||
|---|---|---|
| Organ/Part of Organ | Location/Description | Notes |
| fascia lata (N544, TG3-02) |
deep fascia forming tubular investment of the thigh | thickened laterally as iliotibial tract/band; connected to femur by lateral & medial intermuscular septa; Scarpa's fascia attaches to it below inguinal ligament |
| iliotibial tract (N493, TG3-16, TG3-26, Practical) |
extends from the iliac tubercle to a tubercle on the lateral condyle of the tibia | the conjoint aponeurosis of the tensor fasciae latae and gluteus maximus mm. |
| crural fascia (N544, TG3-02, TG3-03) |
deep fascia forming a tubular investment of the leg | crural fascia is continuous with the fascia lata at the level of the knee; it is connected to the fibula by the anterior and posterior intermuscular septa; crural fascia is thickened near the ankle to form the extensor and flexor retinacula (Latin, crural = the legs) |
| deep dorsal fascia (N544,N545, TG3-02, TG3-03) |
dorsally continuous with the inferior extensor retinaculum | |
| plantar fascia (N544,N545, TG3-02, TG3-03) |
deep fascia of the sole | forms plantar aponeurosis |
Lymphatics |
|||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Structure | Location | Afferents from | Efferents to | Regions drained | Notes |
| superficial inguinal nodes (N546, TG3-70, Practical) |
in superficial fascia parallel to inguinal ligament & along greater saphenous v. | deep inguinal nodes | external genitalia; superficial parts of lower limb | ||
| deep inguinal nodes (N546,TG3-70, TG3-18B |
medial to femoral v. deep to fascia lata & inguinal ligament | superficial inguinal & popliteal nodes | external iliac nodes | lower limb, external genitalia, lower anterior abdominal wall | the deep inguinal node in femoral canal is called node (or gland) of Cloquet |
| The material presented in these tables is contained in the book: MedCharts Anatomy by Thomas R. Gest & Jaye Schlesinger Published by ILOC, Inc., New York Copyright © 1995, unauthorized use prohibited. |
The excellent editorial assistance of Dr. Pat Tank, UAMS is gratefully acknowledged. |